Disruption-Tolerant Wireless Sensor Networking for Biomedical Monitoring in Outdoor Conditions
Texte intégral
Figure


Documents relatifs
In this article, a novel monitoring mechanism is proposed for wireless sensor networks, in which we have proposed a technique for objects detection based on
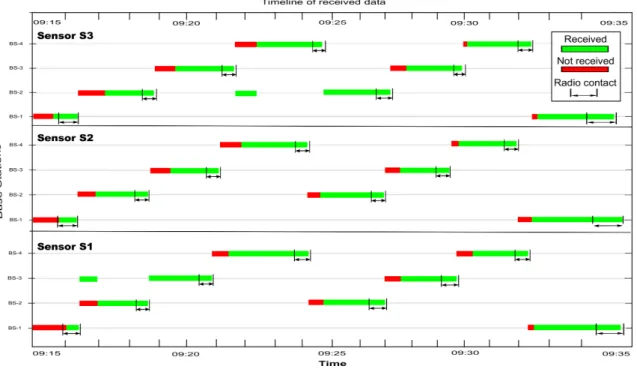
We consider here that the best tracking precision (100%) is obtained when we have one point every five meters (the target speed corresponds to a pedestrian). Figure
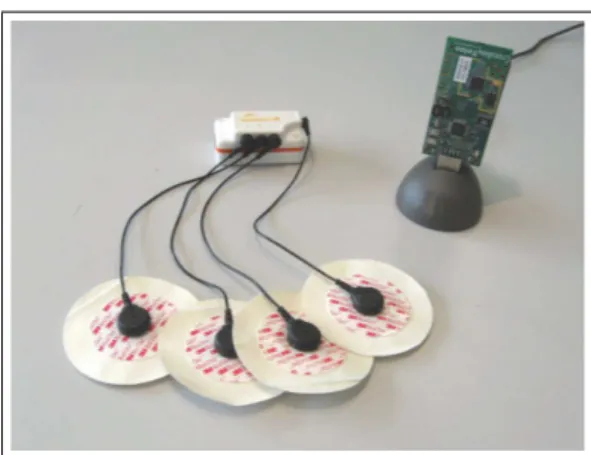
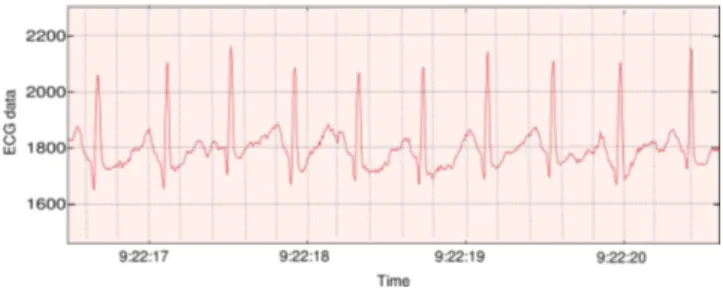
The rapid growth in biomedical sensors, low-power circuits and wireless communications has enabled a new generation of wireless sensor networks: the body area networks.. These
The data collected for the project involves French-speaking CLIL and non-CLIL learners (control group) with Dutch or English as a target language, at different
During this time, the sensor listens to messages sent by neighbors (lines 2&4): When the first receiving the message (line7), then the node will be the child of node
Directed diffusion (DD) was proposed as a robust data- centric dissemination protocol for WSNs in [5]; data generated by sensors are named by attribute-value pairs and all nodes
A Wireless Real-Time Monitoring Node of the Physiological Signals for Unrestrained Dairy Cattle Using Wireless Sensor Network.. Third IFIP TC 12 International Conference on Computer
Lastly, we have shown that the variables measured at the watershed scale (i.e. land use and large scale hydromorphological characteristics) integrate all the types of