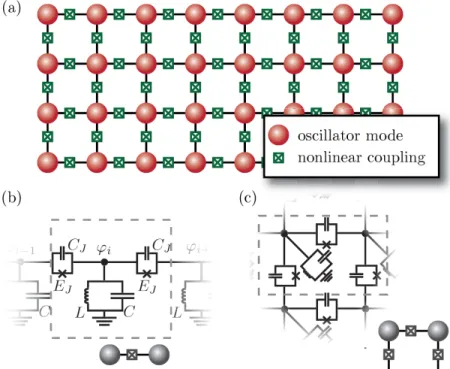
Strongly correlated photons in arrays of nonlinear cavities
Texte intégral
Figure
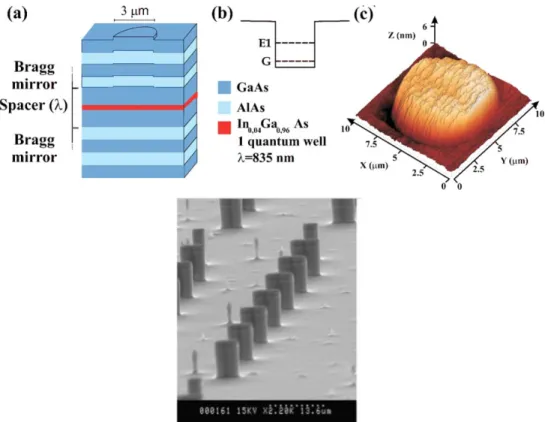
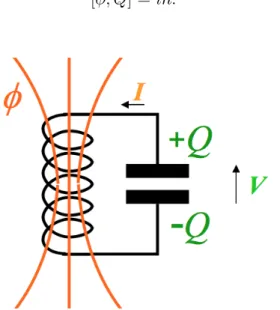
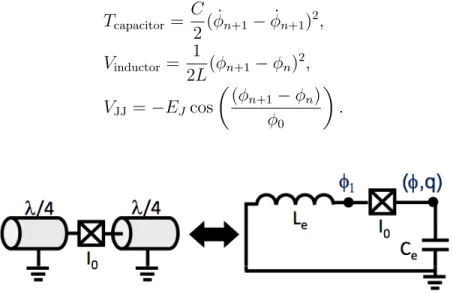
Documents relatifs
Using our induction hypothesis (and working in the outer space of each of the factors that are elliptic in the splitting), we prove that subspaces in CV [ N made of trees that split
The key difference is that while those bounds are typically used to bound the deviation between empirical and expected means under the assumption that the data are drawn from the
Exercice 2.2. You toss a coin four times. On the …rst toss, you win 10 dollars if the result is “tails” and lose 10 dollars if the result is “heads”. On the subsequent tosses,
Moreover, they made in (Critical Gaussian multiplicative chaos: Convergence of the derivative martingale (2012) Preprint) several conjectures on the supercritical case and on
In this article we give a necessary and sufficient condition in order that a measure on a Hilbert space be Gaussian.. We also
In the case when the gauge group is of the form C ∞ (M, G) this study was developed by Gelfand, Graev and Vershik ([8] and [9]), Wallach ([27]), Pressley ([24]) and Albeve- rio
versions of vector spaces, in which you can not only add and scalar multiply vectors, but can also compute lengths, angles, inner products, etc. One particularly common such
Importantly, however, we have shown that the presence of bound states inside the nonlinear medium can be probed with classical light simply by examining higher-order


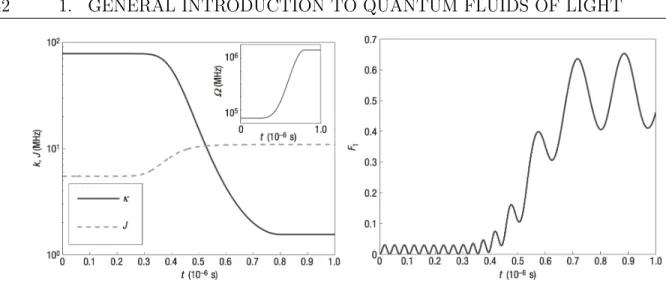
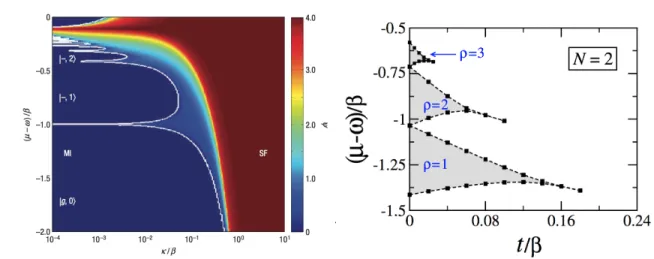
![Figure 1.10: Left: photon fermionization in a 1D array. From Ref.[ 69 ]. Total transmission spectra as a function of the detuning frequency ∆ω p = ω p − ω c](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/2328617.31094/56.918.132.812.122.430/figure-fermionization-total-transmission-spectra-function-detuning-frequency.webp)