Commodity Derivatives: Modeling and Pricing
Texte intégral
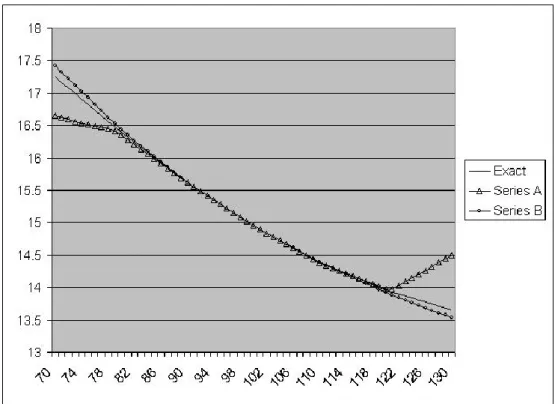
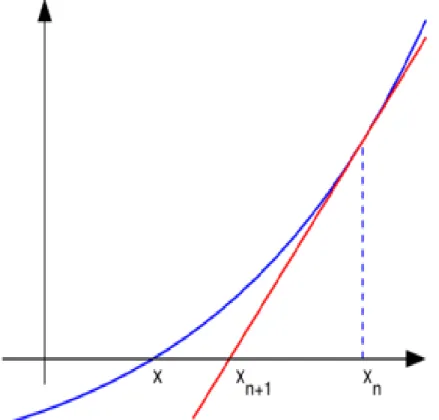
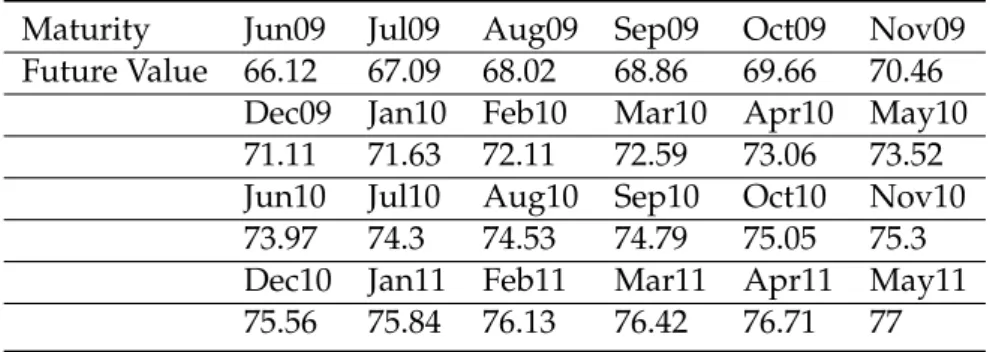
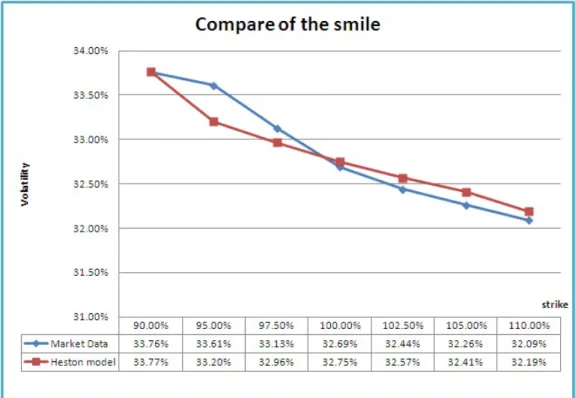
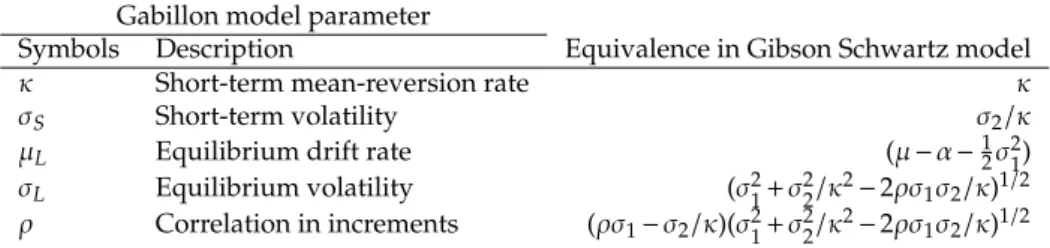
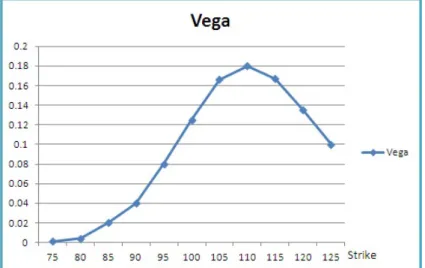
Figure
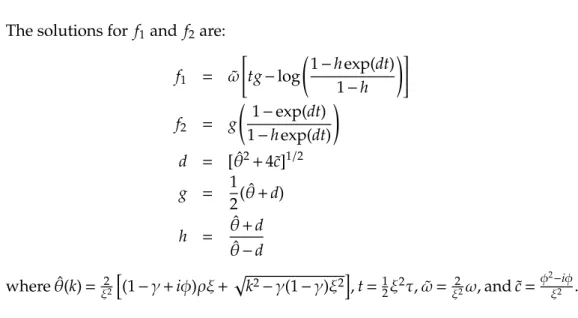

Documents relatifs
Keywords : weather derivatives, arbitrage-free pricing method, actuarial pricing approach, consumption-based pricing model, risk-neutral distribution, market price of risk, finite
To serve as a benchmark, the returns on the Kuala Lumpur Composite Index (KLCI) are employed as a proxy for market portfolio returns, the return from a 3-month
To handle this problem, a two-stage mixed-integer stochastic programming model was proposed to facilitate this multi-commodity redistribution process.. In our model, we define
To accelerate the algorithms we developed parallel solutions to the Longstaff-Schwartz method for lower bound and the Andersen-Broadie method for upper bound, and applied them to
marginal features dichotomy, Kuukkanen distinguishes three possible temporal behaviors of concepts: (i) concept stability: a concept keeps through time both its core and
The plan of this paper is as follows : in section 2, we describe the weather derivatives, in section 3 we present the discrete time long memory processes which are the
The structure of the paper is as follows: section 2 outlines the consumption-based asset pricing model for the weather derivatives, section 3 describes the estimation of the
Section 1 and 2 provide a detailed derivation of the hedging portfolio in a pure jump dynamics for the risky bond, whereas Section 3 deals with the more realistic case of a