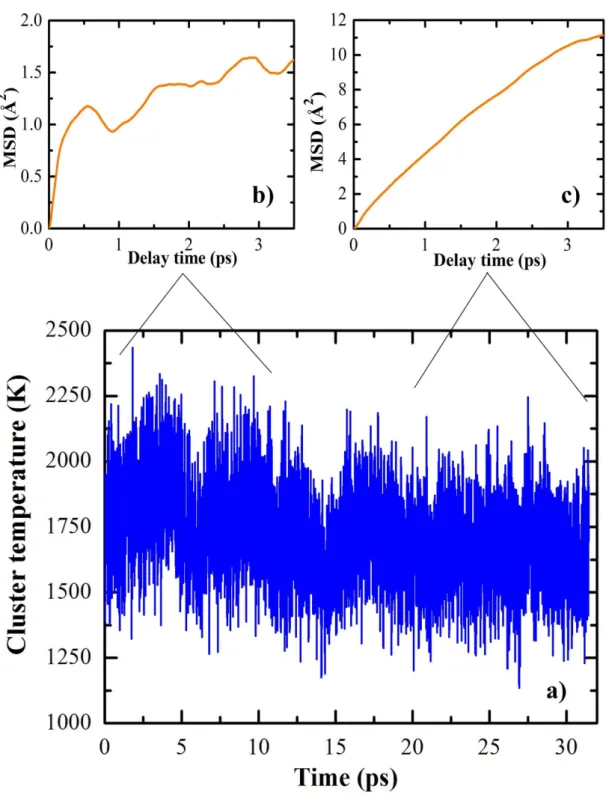
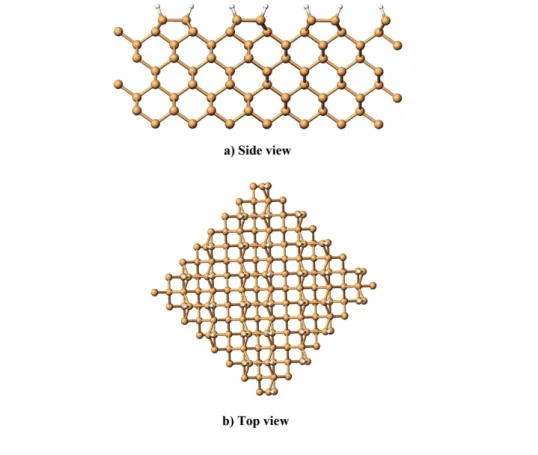
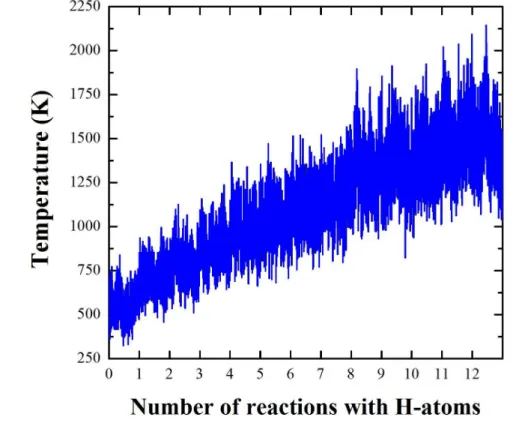
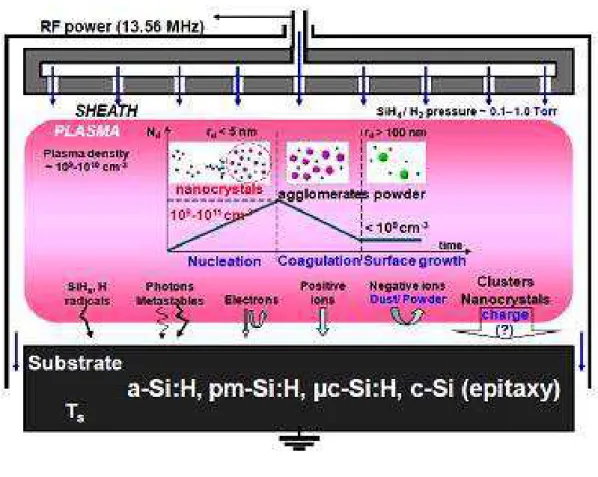
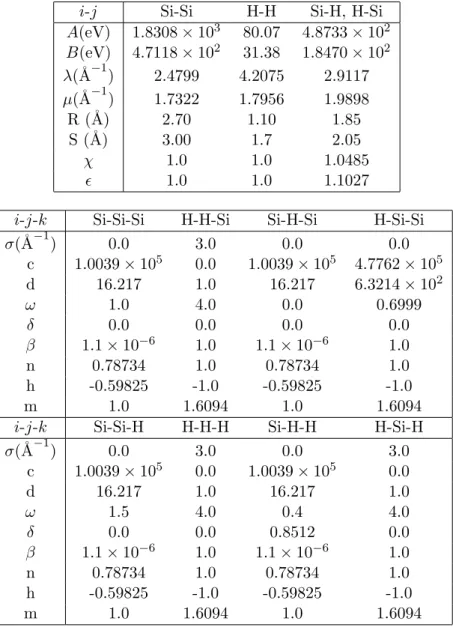
Molecular dynamics simulations of H-induced plasma processes and cluster-catalyzed epitaxial growth of thin silicon films
Texte intégral
Figure


Documents relatifs
Phase II trials showed that 11.8–18.4% of pretreated patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer experienced ORs following treatment with 250 mg/day
From these studies it emerges that this model undergoes a chiral-glass phase transition at a finite temperature [6, 7] while it was for long time believed that the spin-glass
trie substrate. These results confirm that it is possible by this technique to elaborate cermets.. a) Micrograph of a Bi-SiO~ cermet (20 nm thickness). b) Corresponding size
diffraction pattem obtained after the growth of a thick silicon film m the temperature range 300 °C-400 °C, is very different from that given in figure 1. The spotty diagram
Parmi les noms proposés, pour le quadrilatère ci-dessus, entoure ceux qui sont corrects.. CHAT CHTA TCHA TAHC
Endeavouring to better understand the mechanisms of tubulointerstitial injury, we have recently put forward a novel hypothesis that the canonical vitamin A signalling mediated
(2014) showed that the activity of oxidative enzymes was higher in the liver of chickens fed the LL diet by comparison with the chickens fed the HL diet. The lower
L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, émanant des