Links between mechanical behavior of cancellous bone and its microstructural properties under dynamic loading
Texte intégral
Figure


Documents relatifs
In this study, the mechanical and microstructural properties of the synthetic hydroxyapatite, with Ca/p stoichiometry equal to 1.67, were determined as a function of
5.4 Experimental results for DIF as a function of strain rate: for fine-grain concrete with green diamond markers (left) and for fiber-reinforced concrete with blue triangles
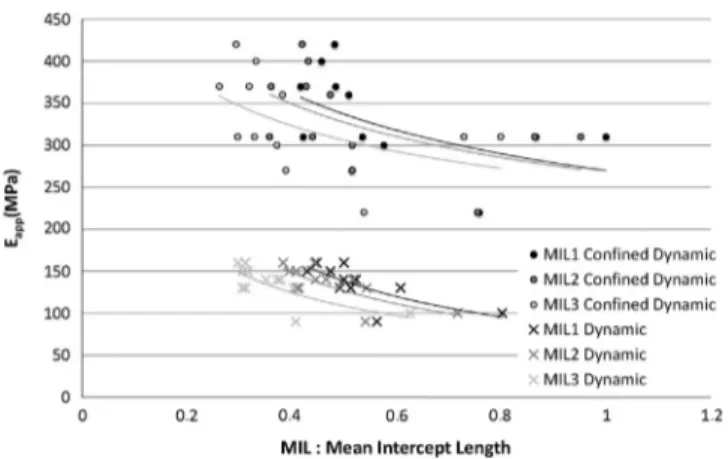
The behavior of bovine cancellous bone under compression is measured as a foam-type behavior over the whole range of strain rates explored in this study (Figure 2a). In this way,
Elle envisage l’appli- cation des règles de conflit exis- tantes en matière de compétence internationale et de loi appli- cable avant d’aborder l’avène- ment de
the MPN, (ii) nonclassical ER␣ signaling is sufficient to rescue rapid phosphorylation of PAK1 in preoptic cells, as well as suppression of LH secretion in ER ␣-null mutants, and
Furthermore, this table shows that more than half of occupational wage changes can be due to industry effects: due to either the reallocation of manual or abstract workers
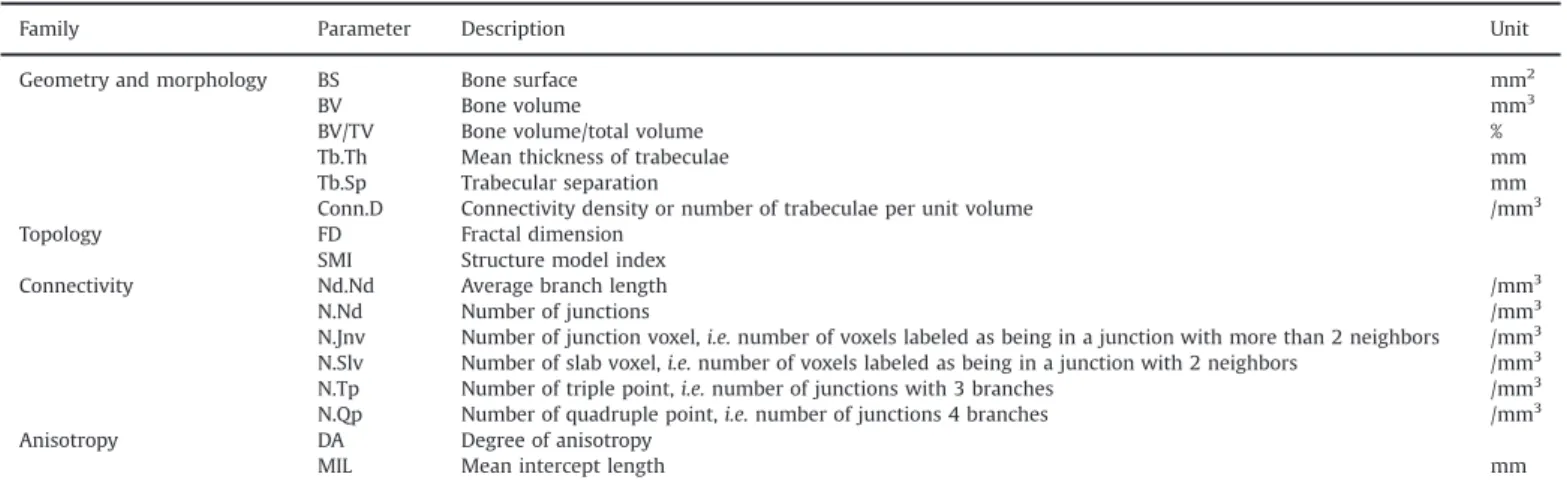
Mechanical elastic properties in the three main directions X, Y, Z and the maximum compressive stress in the direction of the superior trabecular network are shown in Table 1..
The formation of the Langmuir films at the air - water interface was investigated by means of surface pressure - molecular area isotherm, surface potential-molecular area isotherm,