Analyse cinétique et cinématique de la locomotion chez les enfants atteints d'un déficit moteur cérébral : comparaison de l'orthèse tibiale fixe et articulée
Texte intégral
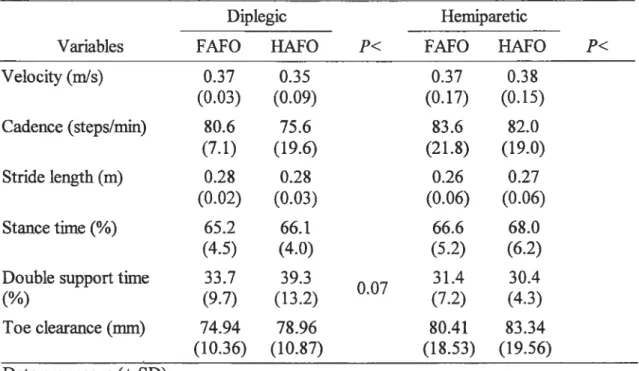
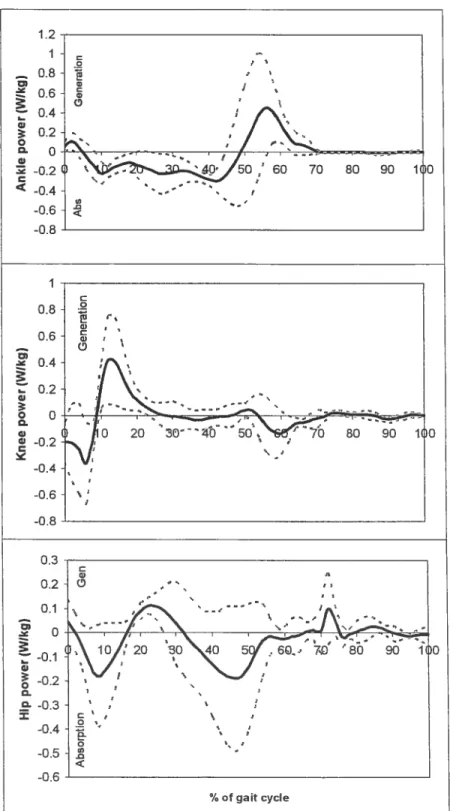
Figure



Documents relatifs
Intramuscular BoNT-A injections reduced the stretch reflex in the MG accompanied by an increase in resting muscle belly length, whereas casting resulted in increased
We modeled altered muscle-tendon properties by personalizing Hill-type muscle-tendon parameters based on data collected during functional movements, simpler neuromuscular control
In cerebral palsy, not all the conserved repertoire can be used; above all, the child is not always able to choose the best motor strategy to carry out a required task in
Clinical gait analysis is widely used in clinical routine to assess the function of patients with motor disorders. The proper assessment of the patient's function relies greatly on
Clinical gait analysis is widely used in clinical routine to assess the function of patients with motor disorders. The proper assessment of the patient's function relies greatly on
Gait was inspected on a vector level (all sagittal motions combined), and an individual joint level (pel- vis, hip, knee and ankle joint motions). Statistical non-parametric mapping
The gross motor function classification system (GMFCS), the gait profile score (GPS), GPSs per motion plane, gait variable scores (GVS) and multiple-joint (MJ) gait patterns
18 Owing to a lack of studies looking at the use of antacids and mucosal protectants in managing GERD in pediatric patients, the 2018 Pediatric Gastroesophageal Reflux