Decision making for smart grids with renewable energy.
Texte intégral
Figure
![Figure A.1 – NIST Smart grid conceptual model 3.0 [1]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/5384358.125076/25.892.231.670.132.580/figure-nist-smart-grid-conceptual-model.webp)


Documents relatifs
The focus of this paper is on the context-aware decision process which uses a dedicated Markov Logic Network approach to benefit from the formal logical representation of
The formalism of semantic knowledge also allows for inconsistency detection, which is a real challenge in the domain of smart city where a piece of data will be used in many
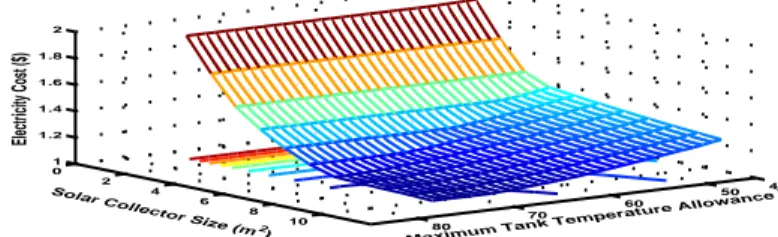
To ensure that the implemented energy management model using MILP is efficient in reducing the total electricity cost in the microgrid, we have compared it with a
Objectives can vary depending upon the type of distributed energy resources being used and they can be based on levelized cost of renewable energy sources, battery degradation
The smart grid concept supports the functioning of such energy systems with the integra- tion of proactive consumers that contribute to the energy generation through their own
Using continuous radar measurements with the AL- WIN radar at Andenes and the ESRAD radar near Kiruna, we found, that the strongest gravity wave activity in the tropo- sphere
Nihoul, M 2015, La liberté d'expression académique des acteurs de l'enseignement et de la recherche (enseignants, chercheurs, étudiants) selon la Cour européenne des droits de
Donc, en corrigeant cette erreur matérielle et en appliquant le texte de droit selon son esprit – inchangé –, la solution est la suivante: lorsque la décision de retrait a


![Figure 1.1 – NIST Smart grid conceptual model 3.0 [1]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/5384358.125076/71.892.233.671.137.564/figure-nist-smart-grid-conceptual-model.webp)