Rapid characterization of aquatic hyphomycetes by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry
Texte intégral
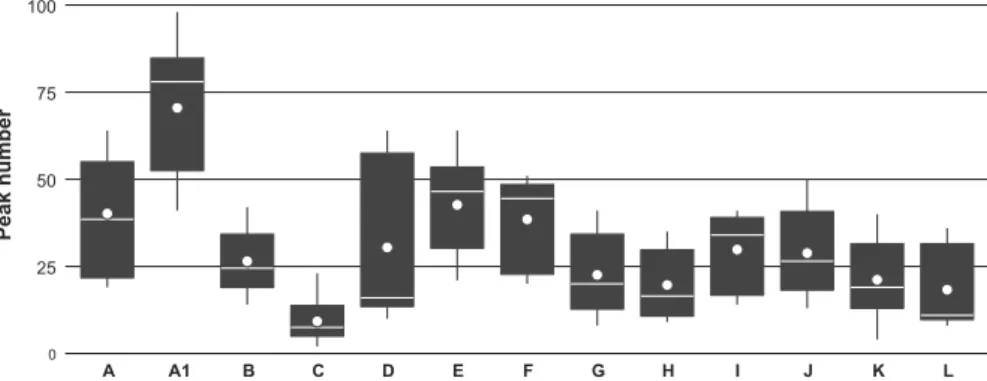
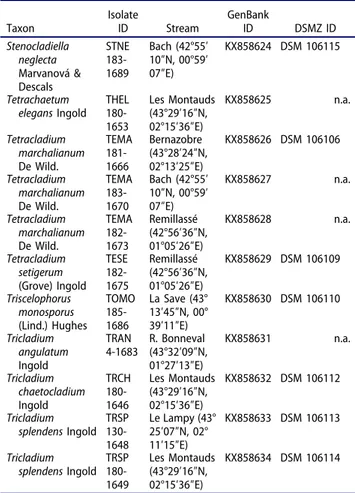
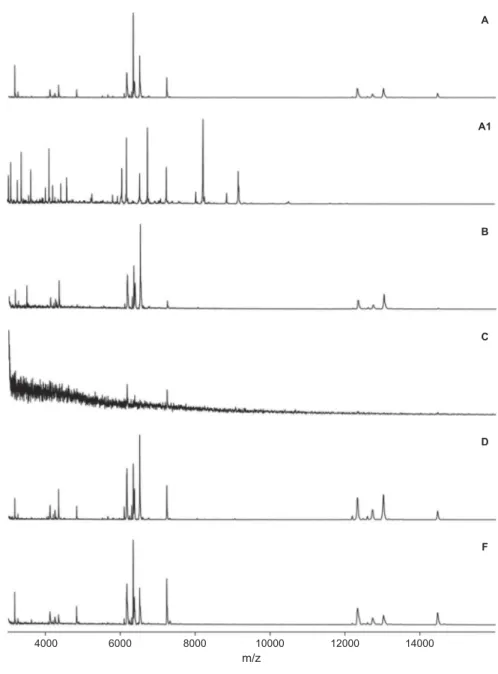
Figure


Documents relatifs
Identification of Streptococcus agalactiae isolates from various phylogenetic lineages by matrix-assisted laser desorption ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry..
Confident identification of filamentous fungi by matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry without subculture-based sample preparation.. Arnaud Riat
Potential of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization time-of-flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF MS) for the identification of freshwater zooplankton: a pilot study with
The imipenem hydrolysis assay was performed blindly twice on the 149 strains listed in Table 1 using the two criteria listed above, i.e., the disappearance of the peak at 300.0
As for direct identification using MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry directly on blood culture bottles samples were anonymized and results obtained by using the protocol presented herein
Direct MALDI-TOF mass spectrometry assay of blood culture broths for rapid 151. identification of Candida species causing bloodstream infections: an observational study
assisted laser desorption ionization-time of fl ight mass spectrometry methods with conventional phenotypic identifi cation for routine iden- tifi cation of bacteria to the
In a low prevalence area for extended spectrum betalactamases (ESBL) and multiresistant gram- negative bacteria, MALDI-TOF performed on blood culture pellets had an impact on