Schwarz methods and boundary integral equations
Texte intégral
Figure




Documents relatifs
Title: H-matrix based Solvers for 3D Elastodynamic Boundary Integral Equations Keywords: Boundary Element Method, H-matrices, Adaptive Cross Approxima- tion, Randomized Singular
– The paper is devoted to one-dimensional nonlinear stochastic partial differential equations of parabolic type with non homogeneous Dirichlet boundary conditions of white-noise
NIRENBERG, Estimates near the boundary for solutions of elliptic partial differential equations satisfying general boundary conditions
tions of elliptic partial differential equations satisfying general boundary condi- tions, I, II, Comm.. FRIEDMAN, The obstacle problem for the biharmonic
Estimates near the boundary for solutions of elliptic partial differential equations satisfying general bonudary
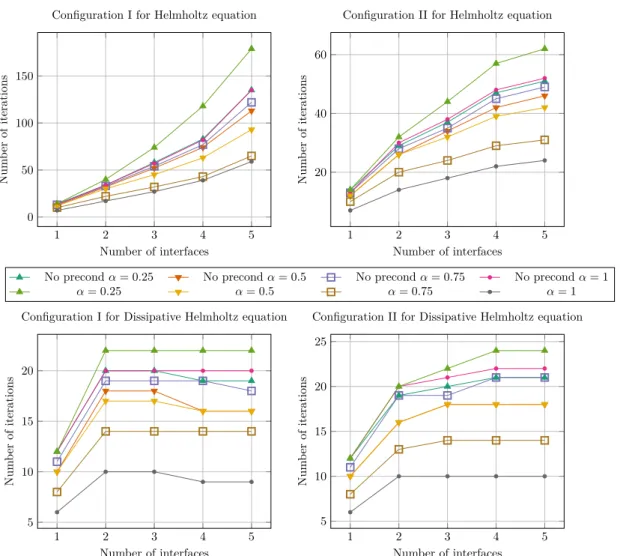
We have shown that for Maxwell’s equations, a classical Schwarz algorithm using characteristic Dirichlet transmission conditions between subdomains has the same convergence behavior
Entropy methods in partial differential equations: fast diffusion equations –
Keywords: acoustic scattering, indirect boundary integral equations, combined eld integral equa- tions (CFIE), coercivity, boundary element methods, Galerkin