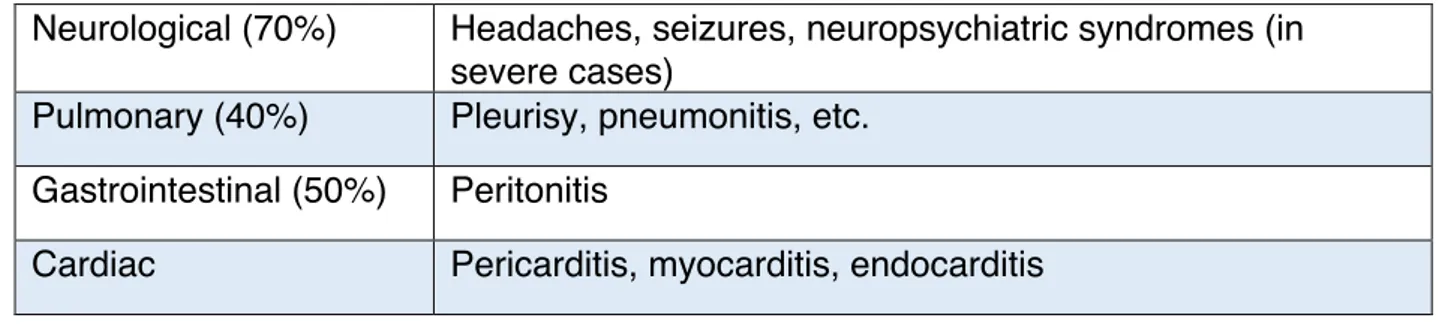
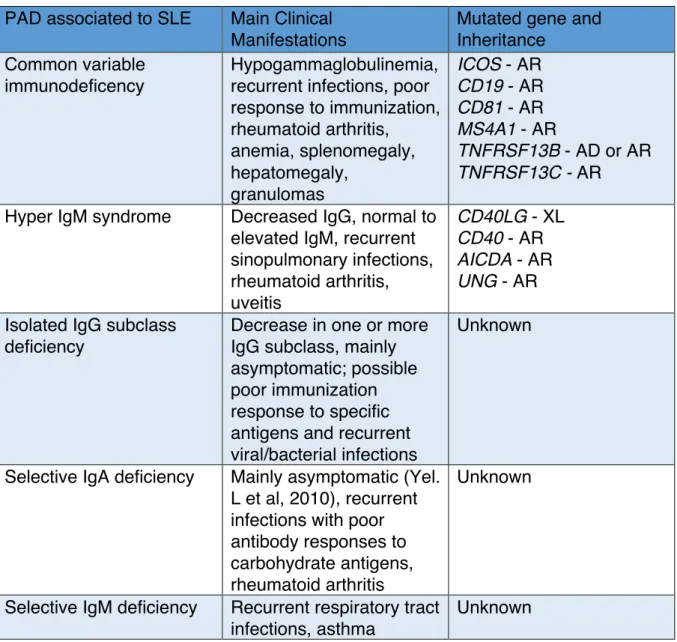
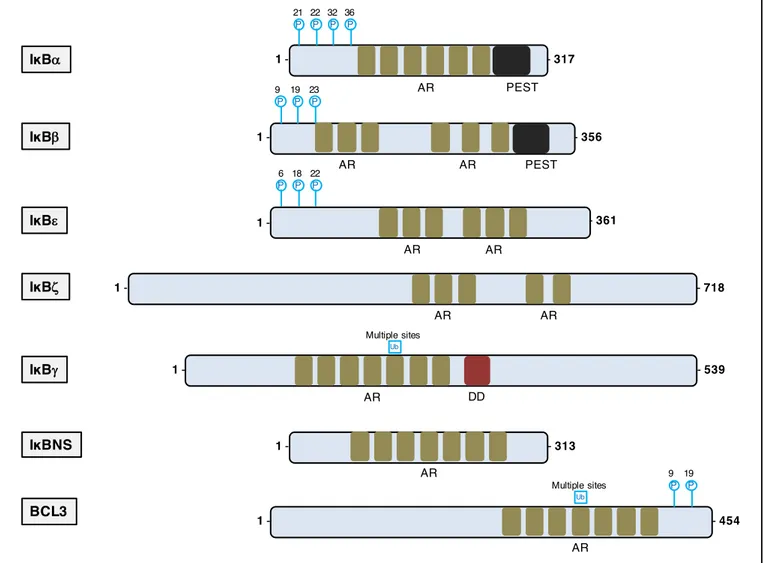
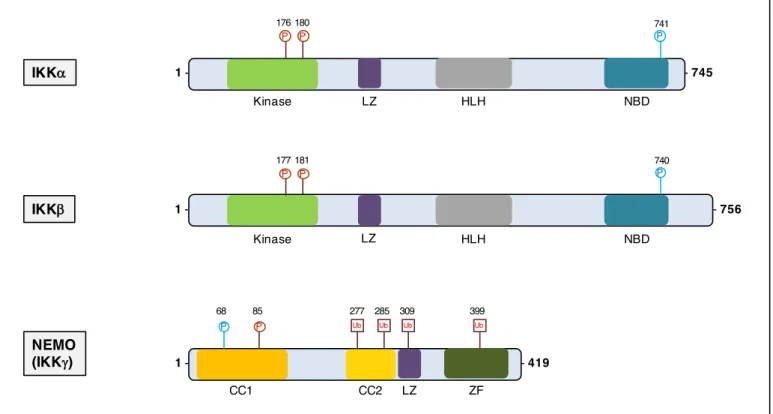
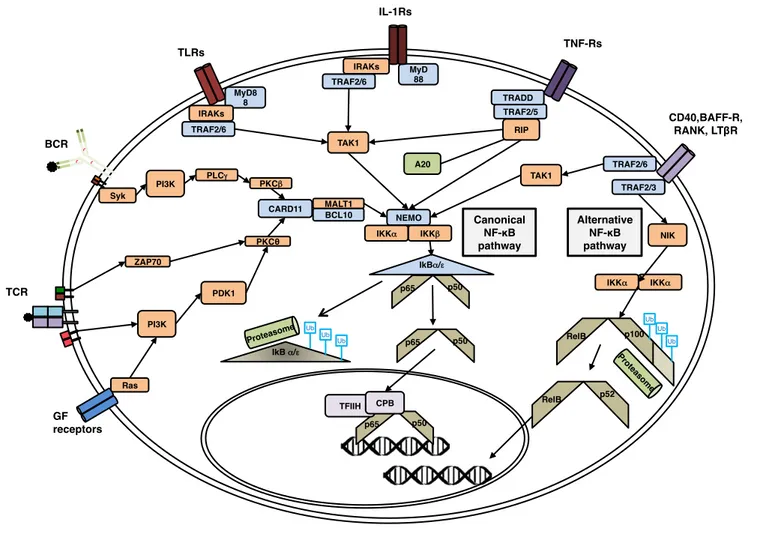
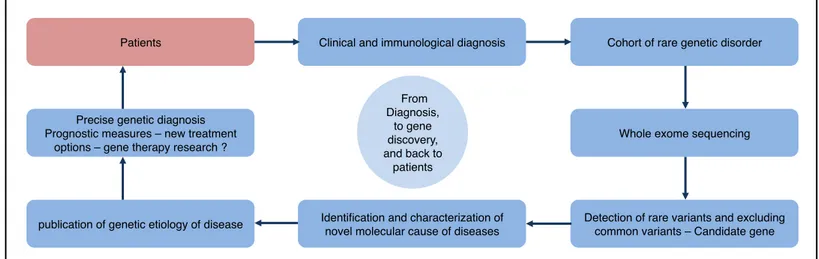
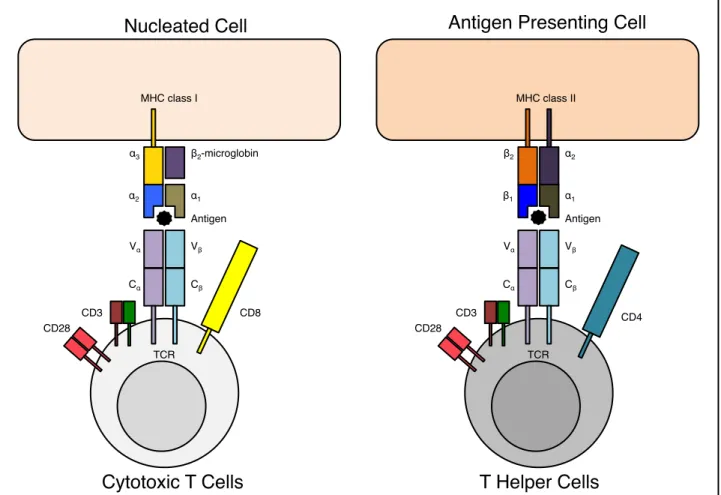
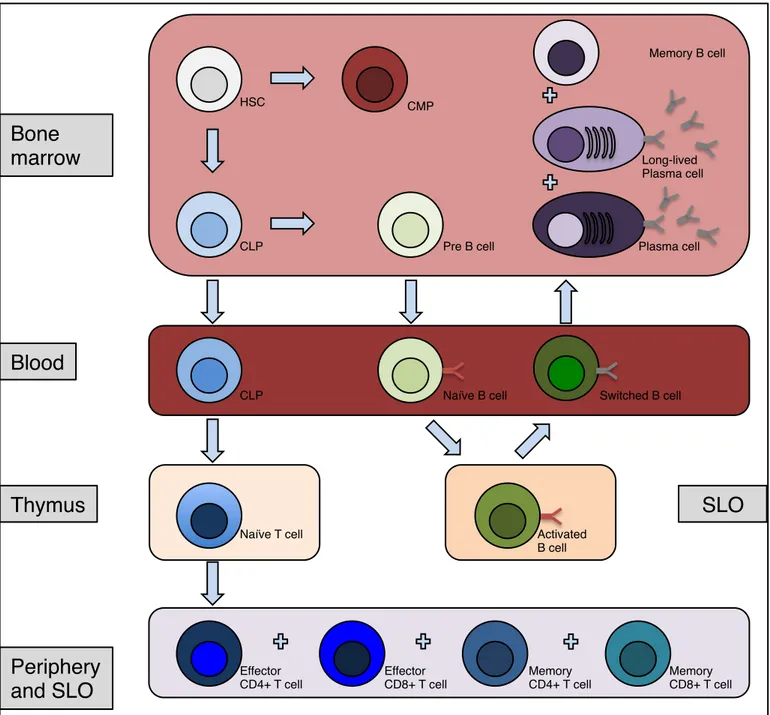
Identification and characterization of novel molecular causes of primary immunodeficiency : RELA mutations are associated to common variable immunodeficiency and systemic lupus erythematosus
Texte intégral
Figure
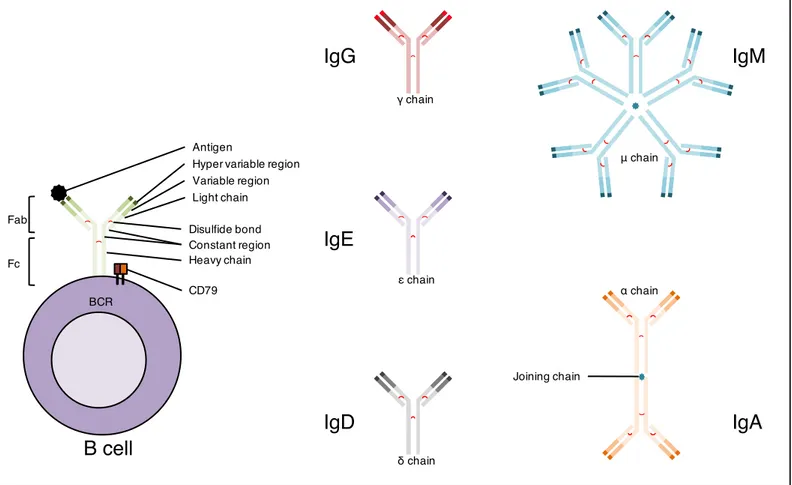
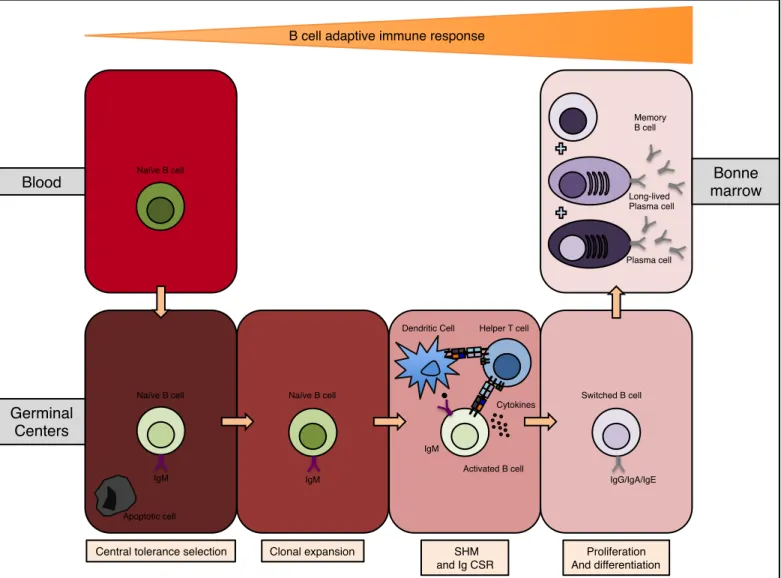
Documents relatifs
Our contributions in this paper include a) We show the data of a novel mobile phone based experiments on the app in- stallation behavior; b) We illustrate that there are strong
Information on the magnitude of the random errors associated with individual match events can be obtained from the scatter of the corresponding ozone mixing ratio di fferences
– La Friction : En frottant deux bâtons pour obtenir de la chaleur – La Percussion : en frottant deux silex pour obtenir des étincelles. Savoir que l’Homo
This study demonstrates in a model of severe acute lung injury by ischemia and reperfusion that ebselen pretreat- ment results in a clearly improved gas exchange of the
As in colliculi neurons, the time course of 5-HT 4 R–induced p-ERK1/2 accumulation observed in HEK293 cells was very transient with a maximum effect after 5 min of stimulation, and
As systemic manifestations are also reported in patients with PAPS, and as a subgroup of PAPS patients could evaluate to a SAPS, the differentiation between the two types of APS
The p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) cascades are major signaling pathways that regulate several functions of endothelial cells in response to exogenous and
Lower phosphatase and tensin homolog deleted on chromosome 10 (PTEN) expression in human basal-like cancers (BLCs) compared with human epidermal growth factor receptor