Interactive Illustrative Line Styles and Line Style Transfer Functions for Flow Visualization
Texte intégral
Figure

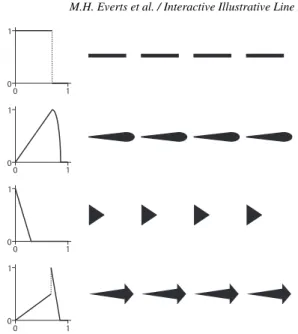
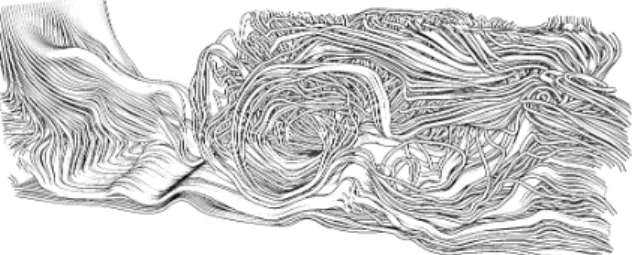
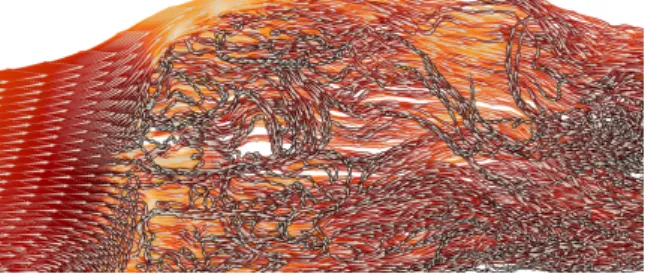
Documents relatifs
The usual concept of stochastic ordering between probability distributions has been ex- tended to belief functions on the real line, resulting in four distinct ordering relations
In the theory of scattered data interpolation with linear combinations of translates of a basis function, we have to deal with strictly positive definite functions rather than
As before /I/ along with those on the inter- mediate valence (IV)-compound (YbCu2Si2) we have performed measurements on a diamagnetic compound (LaCu2Si2) and a compound with a
- In resonance and relaxation studies of polycrystalline ferrites and garnets, size depen- dent contributions arise from effects due to eddy current,
We derive a perspective projection matrix for 3D lines expressed in Pl¨ucker coordinates and a joint projection ma- trix mapping a 3D line to a set of image lines in the second set
As in the case of the classical approach of rhythmic tiling canons construction by fac- torization of cyclic groups, the polynomial approach nat- urally leads to some still
We order the edges with respect to an increasing number of minimal configurations and generate the configuration variables and the associated constraints iteratively as long as
Since our potential, q, and the expected solutions decay exponentially at infinity, it is convenient to truncate the infinite spatial domain to a periodic interval T (−L, L), and
