An Inertial Newton Algorithm for Deep Learning
Texte intégral
Figure
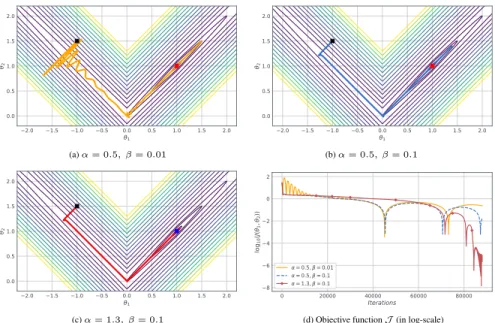
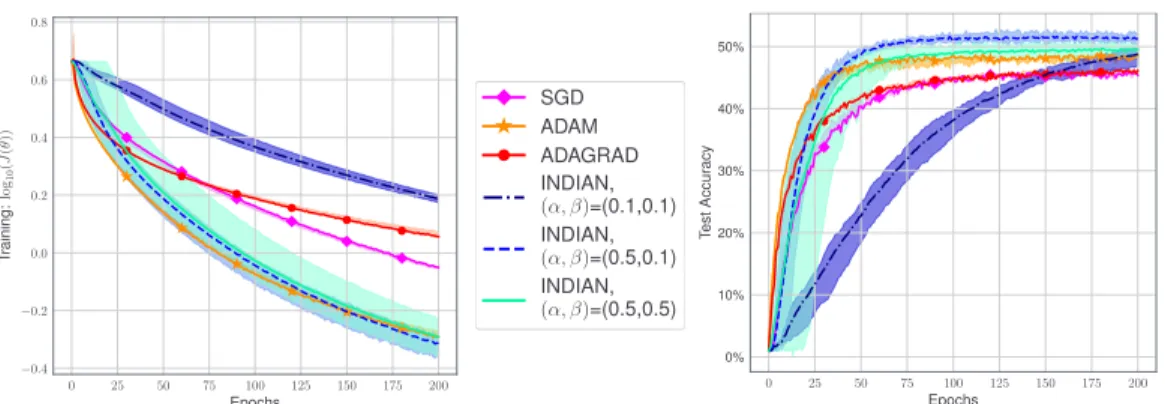
Documents relatifs
In this work, we propose a multi-task model which explores deep learning, and more specifically recurrent neural networks to process AIS data stream for multiple purposes:
An algorithm for generating invisible data poisoning using adversarial noise that breaks image classification deep
We present a new algorithm for learning iteratively generating functions that can be translated at all positions in the signal to generate a highly redundant dictionary.. The main
Local learning algorithms can require a number of training examples exponential in the input dimension to obtain a given generalization error.... Curse
Recent works have applied Deep learning techniques to Knowledge tracing (Deep Knowledge Tracing – DKT) in order to model single student’s behavior during the time, in terms of
We may consider a positive-definite approximation of the Hessian matrix such as the Gauss-Newton matrix [Schraudolph 2002] used in deep learning [Martens 2010], but such an approach
It is based on alternating a quasi-Newton gradient descent for learn- ing the kernel weights and a classical SVM solver for the sample weights; (2) We discuss about convexity for
In this paper, we propose an alternative strategy to stochastic gradient algorithms, in the spirit of the Newton algorithm, in the sense that the step sequence of stochastic