Colour polymorphism is associated with lower extinction risk in birds
Texte intégral
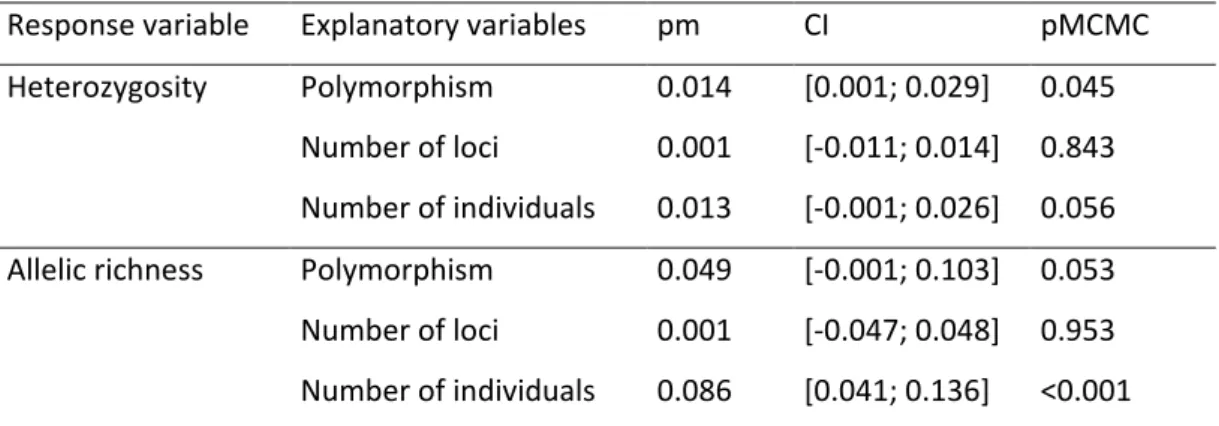
Figure


Documents relatifs
Although specialists in cognitive psychology agree on the importance of a clinical data collection framed by early relevant diagnostic hypotheses, it is frequently observed
Ventral region — Suture between genital and aggenital plates reaching the level of setae g 7 ; nine pairs of genital setae (g) present, among which four pairs in progenital
poroids iv3 present on the posterolateral extensions of sternal shield; exopodal plate behind coxa IV large and triangular, more or less contiguous with but separate from
eucricotes (Figure 2A) (from Lotfollahi et al. 2017) — Prodorsal shield with design almost absent, with very short median and admedian lines near rear prodorsal shield margin as
Specifically, we com- pared occurrence data from the last stage of invasion (independent validation points) to the climate suitability distribution predicted from models calibrated
We propose a statistical framework that allows an additional but ecologically meaningful dimension reduction of joint species distribution models and includes prior knowledge in
cinerea inoculation, all plants were kept under humid conditions (n = 32; 6SE); the experiment was repeated twice with similar results.. By removing oxalic acid released by B.
In fact, as might have been expected, it has been previously demonstrated that a specific expression of the extrapolation of the species accumulation curve