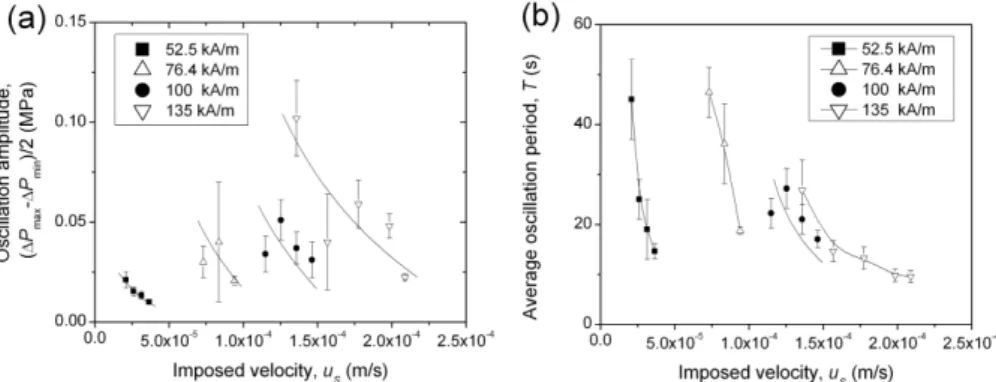
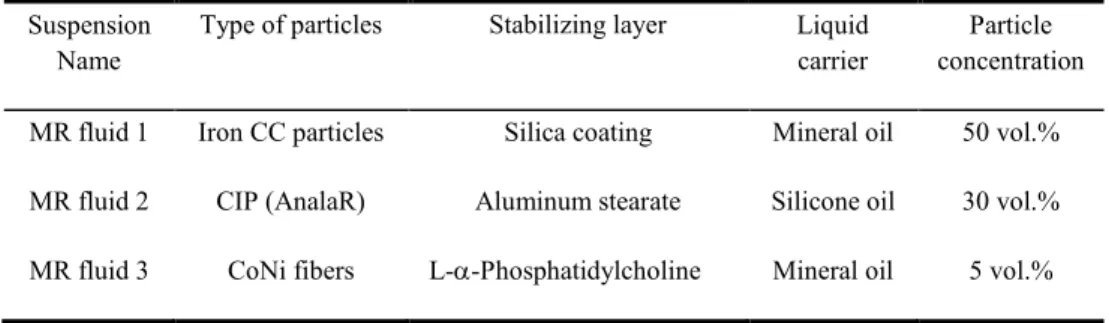
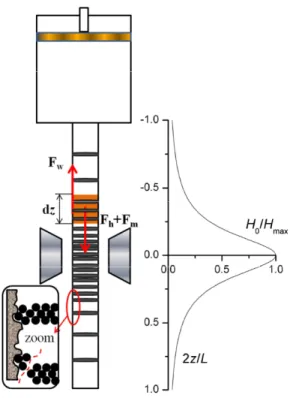
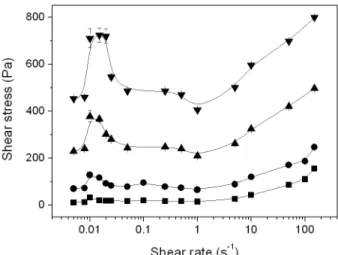
Stick-slip instabilites in magnetorheological fluids
Texte intégral
Figure
Documents relatifs
(local) feature-based. Image-based approaches use global fa- cial cues such as skin colour, head geometry and motion. They are robust to head rotation and scale and do not require
However, the entire process is of very complex nature due to many involved physical and chemical phenomena such as gas flow through the void space in the bed, heat and mass
Moreover, the metric dimension of a special tree, different from a single edge (that could only be obtained when starting from a path), is equal to the number of leaves minus the
Figure 2: Runtime Requirements monitoring framework of adaptive e-learning systems Requirements Monitoring Learning materials repository Questionnaires Log files Scores
Nous avons appliqué notre méthode à 16 séquences d’images réelles de microscopie TIRF représentant des cellules où respectivement les protéines TfR et Langerin ont été
Since high degree nodes found in the heavy tails are in many cases very important to characterize the structure and dynamics of complex networks, we propose the tail-scope method,
Taelman R.-Foot ball nouvelles techniques d’entrainement, Paris :2000.-p.. • ﺔﻴرﺎﺠﻔﻨﻻا ةوﻘﻝا : لوﻘﻴ كﻴﺒﻝأ ﻲﻬﻴﻓ ﻲﻠﻋ ﺎﻬﻨﺄﺒ ﺔﻴرﺎﺠﻔﻨﻹا ةوﻘﻝا ﻰﻠﻋ " ﻲﻓ
In contrast with forms of anemia in which hepcidin is suppressed, patients with iron-refractory iron deficiency anemia (IRIDA) 3 , a disease caused by mutations in



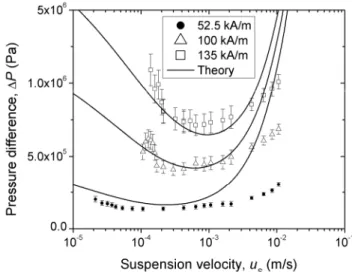
![Figure N.5d as an example). In this case we only observe some small oscillations, associated to the instrumental error [LOP 13]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/13271646.397564/14.892.194.698.454.827/figure-example-observe-small-oscillations-associated-instrumental-error.webp)