Cysteinyl leukotriene signaling through perinuclear CysLT(1) receptors on vascular smooth muscle cells transduces nuclear calcium signaling and alterations of gene expression.
Texte intégral
Figure
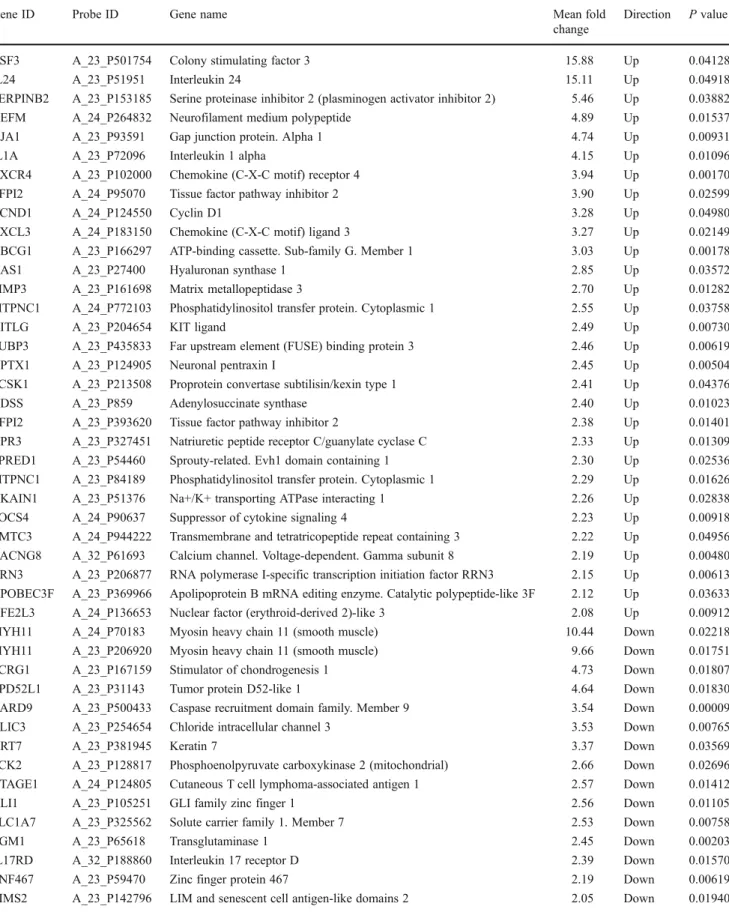
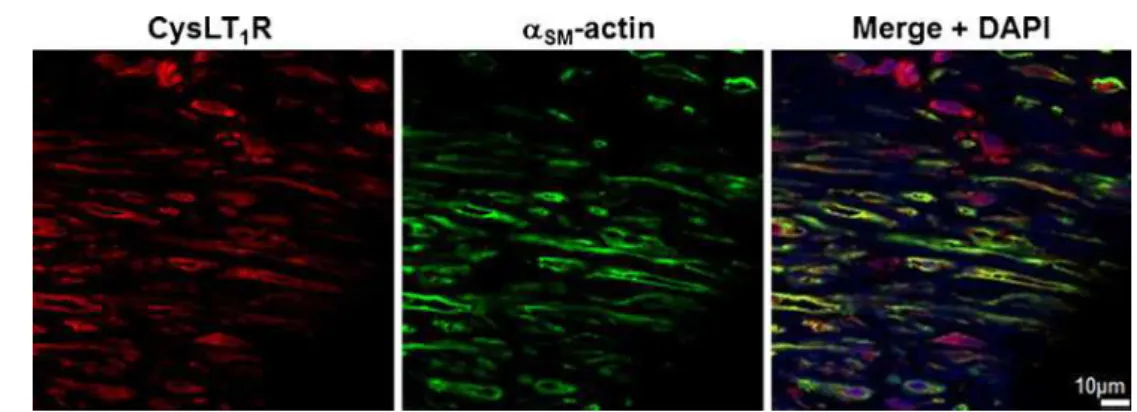
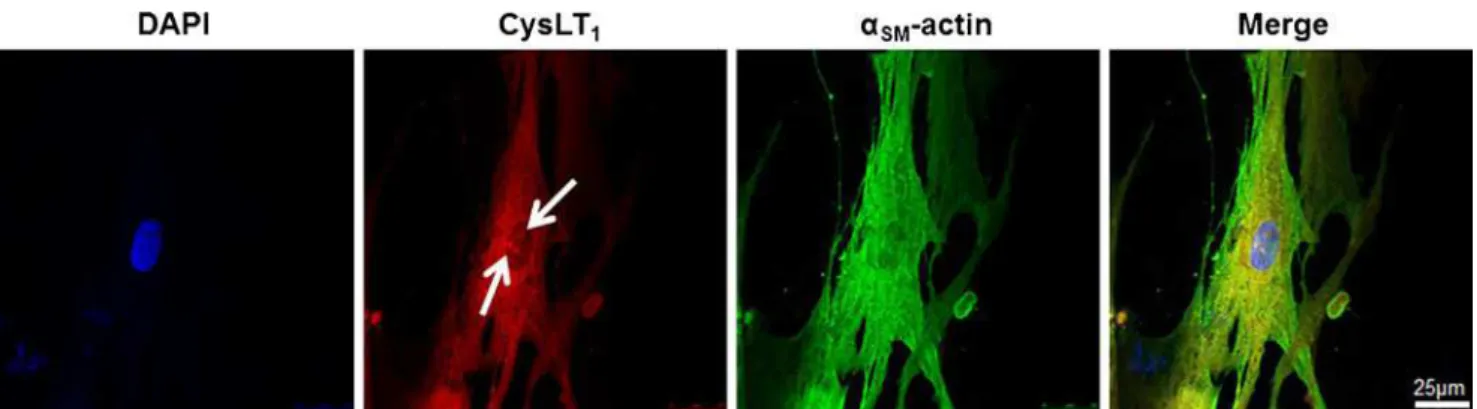
Documents relatifs
different European regions and spine surgeons of the SSE, the study attempted (1) to identify the most important domains determining a good outcome from a patients’ as well as
Note also the following: (i) up to small differences reflecting the attribution of the interaction terms, the scale effect will be the same across all data bases since the
Images des pi` eces de monnaie provenantes de la Banque Centrale Europ´
Following on these observations, our analyses of NOTCH muta- tions from bladder cancer patients, mouse genetic models, cell- based assays, and human cancer samples provide
In this method, we insist on treating seriously the fundamental structures of both the process calculus and the logic, the fundamental example being that typing is preserved both
Chronic exposure to cadmium induces TRPM7 overexpres- sion at the plasma membrane of human epithelial cells leading to increased divalent cation influx, including cadmium influx.
Calcium signaling and β2-adrenergic receptors regulate 1-nitropyrene induced CXCL8 responses in BEAS-2B
Collectively, these data suggest a crucial role for T-type channel activation and SR calcium signal in smooth muscle cell death induced by KDGEA.. This study could give new