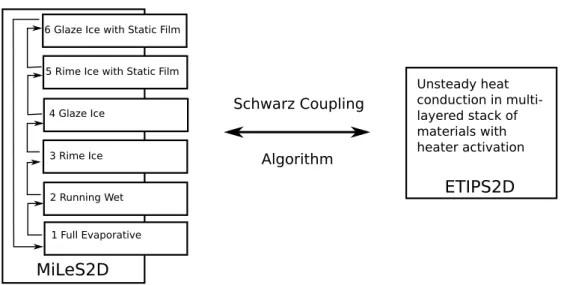
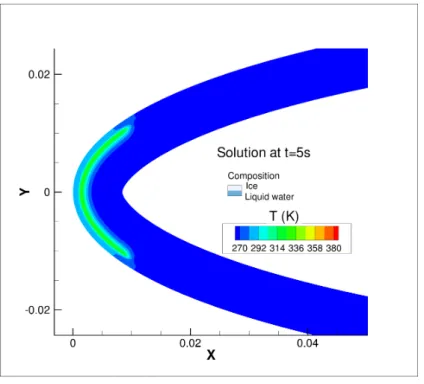
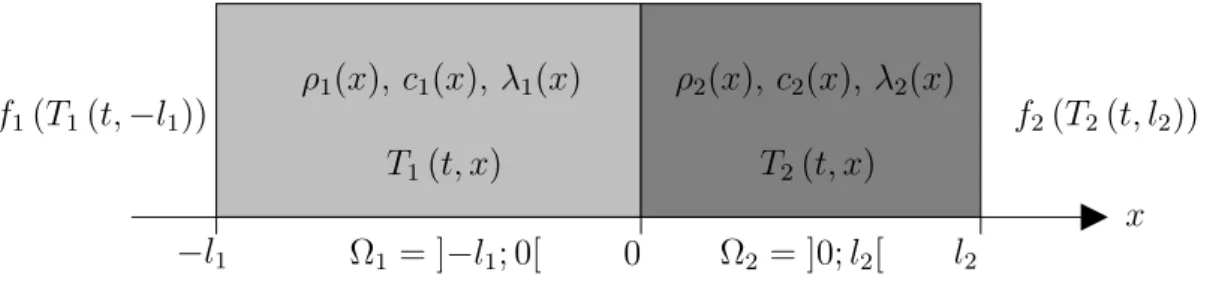
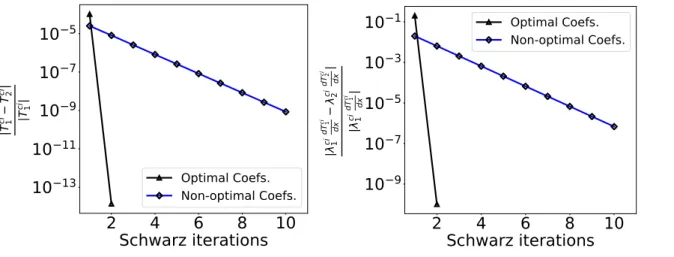
A non-overlapping optimized Schwarz method for the heat equation with non linear boundary conditions and with applications to de-icing
Texte intégral
Figure


Documents relatifs
The question of ε-approximated insensitization comes in general to solve an approximate controllability problem, leading to derive a unique continuation property (see [25, 18], in
— We consider the Schrödinger equation on a half space in any dimension with a class of nonhomogeneous boundary conditions including Dirichlet, Neuman and the so-called
The qualitative behaviour of the solutions exhibits a strong analogy with the porous medium equation: propagation with compact support and finite speed, free boundary relation
Namely, all positive solutions blow up in a finite time if the exponent p pc while global solution exists if p > pc and initial value is small enough.. As part
The Carleman estimate proven in Section 3 allows to give observability estimates that yield null controllability results for classes of semilinear heat equations... We have
The proof for null controllability for the linear parabolic heat equation is then achieved in [11] for the case of a coefficient that exhibits jump of arbitrary sign at an
The Carleman estimate (3) allows to give observability estimates that yield results of controllability to the trajectories for classes of semilinear heat equations.. We first state
The Carleman estimate (5) proven in the previous section allows to give observability estimates that yield results of controllability to the trajectories for classes of semilinear