Viral ecology of organic and inorganic particles in aquatic systems: avenues for further research
Texte intégral
Figure
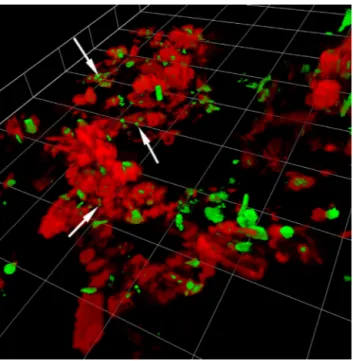
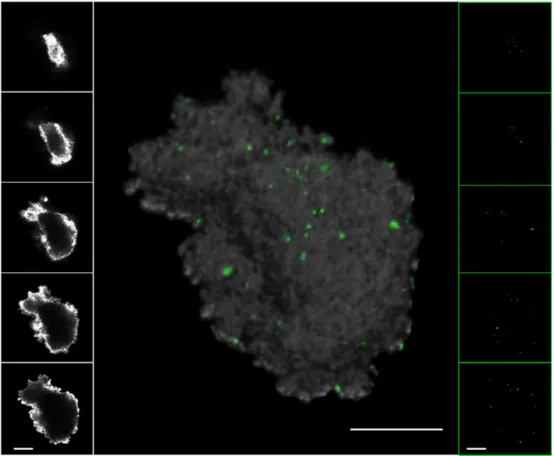
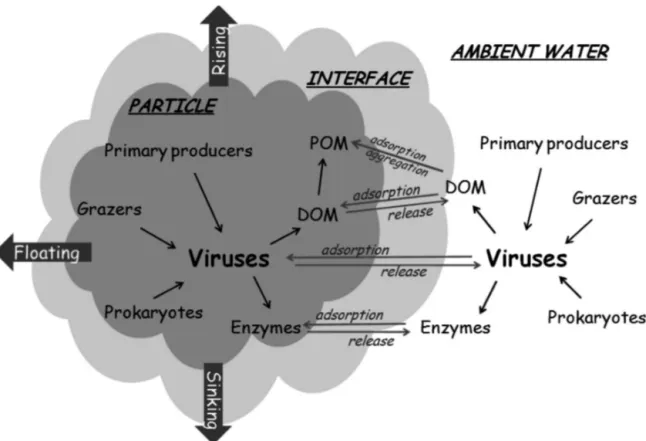
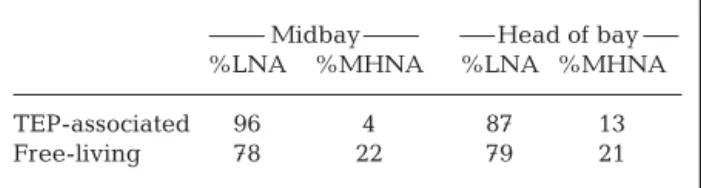
Documents relatifs
Trends in digits that were consistently read incorrectly were identified, and the error rate per digit (0 through 9) was calculated by dividing the number of times the digit
Much has been stated about the potential risks of nasal lavages (NL) during the coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) pan- demic for COVID-19 patients and surrounding people..
HBV DNA detection and quantification is useful in clinical practice to: (i) to diagnose chronic hepatitis B with viral replication; (ii) establish the prognosis of liver disease
Verantwortlich fu¨r diese physiologische Anpassungsreaktion seien, so Selye, die Hormone der Nebennierenrinde, mit deren Strukturaufkla¨rung sich um 1936 verschiedene Chemiker
To achieve our objective, we assessed the abundance and viral community composition in these four regions, and examined their potential relation to an array of (1)
At fine scale, JEV ecology is indeed largely affected by both land cover and land use as these factors affect vectors’ and hosts’ ecology (Figure 1). Once the JEV is introduced,
(1) methods detecting organic molecules and the interactions of such molecules with viral particles (methods at the molecular level), (2) methods focusing on the localization
Our results suggest that the H5N1 polymerase gene segments, and to a lesser extent the NS gene segment, contribute to cytokine hyperinduction in human macrophages and that a putative