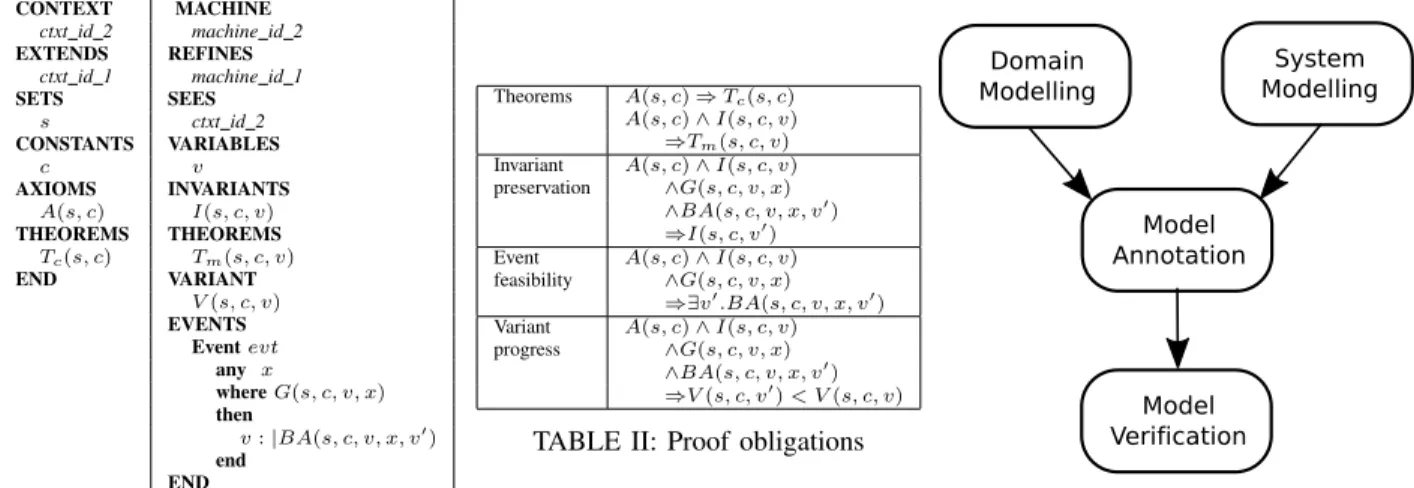
Formal Ontology Driven Model Refactoring
Texte intégral
Figure



Documents relatifs
Here we report on the usage of patterns applied to two biomedical ontolo- gies: firstly a novel ontology for karyotypes which has been built ground- up using a pattern based
At the software side, we intend to develop an Eclipse plugin implementing a fully- automated sub-process for applying refactoring actions, based on model differencing, that will
Most previous logit assignment models have used Dial's second definition of efficient paths, according to which "a path is efficient (reasonable) if every link in it
To be able to specify these refactoring operations on a higher abstraction level as proposed in the Java Refactoring Case at the Transformation Tool Contest (TTC) 2015, we propose
To solve this, SDMLib provides a recursive descent parser that analyzes java source code files and create an abstract graph model.. Using the parser is really easy due to the fact
Since more than a decade, Performance Antipatterns [5,6] revealed to be strong support for performance-driven software model refactoring, since they have been used to: (i) “codify”
However, if the devel- oped model is rather complex, covers multiple domains, the computation-independent model (describing real-world objects rather than particular sets of
Keywords: Business Information System, Business Knowledge Model, Domain Model, Model Driven Design, Innovation, Information Engine.. 1 IT based Information Systems
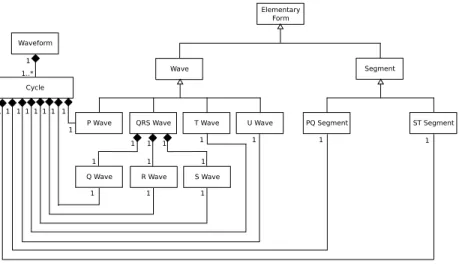
![Fig. 10: Taken from the old ECG model [9]](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/14346935.500213/10.918.144.388.155.460/fig-taken-from-the-old-ecg-model.webp)
