Muscle satellite cells are functionally impaired in myasthenia gravis: consequences on muscle regeneration
Texte intégral
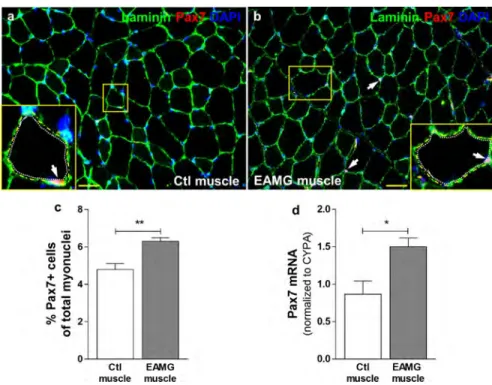
Figure



Documents relatifs
Suite à la réalisation des différents plans de traitement, nous avons réalisé les HDV correspondants pour les trois PTV correspondant au trois niveaux de dose (PTV1, PTV2 et PTV3),
There was little evidence of replication of pre-existing myocytes, indicating that natural cardiac regeneration in the mouse occurs primarily through stem or progenitor cell
“Stories About not Being Afraid of Ghosts” did not only renew the relevance of ghost stories to modern China, it also demonstrated the high malleability of (literary) ghost
Toujours in vitro, nous avons montré que les macrophages pro-inflammatoires (mimant les monocytes/macrophages Gr-1 + CX3CR1 lo recrutés) stimulent fortement la prolifération
Then, the comprehensive knowledge on redox regulation of MuSCs and their surrounding cell partners (macrophages, endothelial cells) during skeletal muscle regeneration
Enhanced skeletal muscle growth is also observed in animals with the Carwell (or rib-eye muscling) mutation, and a double-muscling phenotype has been documented for animals of the
Conclusion: Although sirolimus stimulates TF protein expression in human SMC associated with inhibition of mTOR, it does not enhance TF activity released from the cells, suggesting
plying muscle satellite cells with existing fibers, suggests that satellite cells from those selected lines may have different growth potential. Satellite cells were



