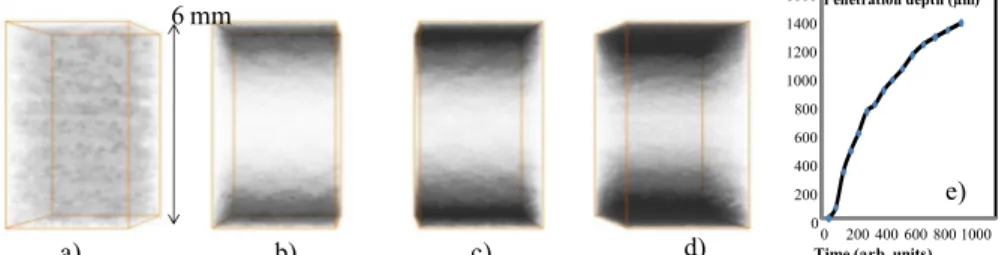
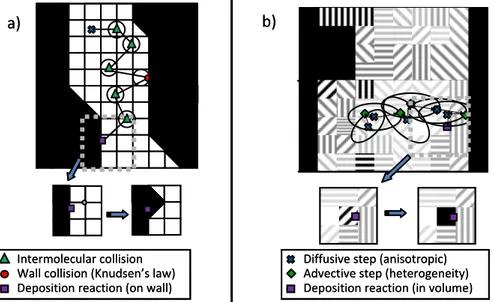
Modelling Chemical Vapour Infiltration in C/C composites: numerical tools based on µ-CT images
Texte intégral
Figure



Documents relatifs
Although the HDPE nets could not be directly treated by PICVD, this simulated behaviour demonstrates that, if the UV pro- tector issue can be curtailed, a 120° contact angle should
The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in the credit line; if the material is
The simplest system to grow CNTs by CCVD consists of catalyst nanoparticles brought to high temperature in presence of gaseous carbon-containing molecules. The nanoparticles are
Pour les infections urinaires chez cette population, le traitement choisi devrait idéalement être le plus spéci- fique possible afin de limiter l’émergence de résistances et
7 - Logarithmic plot of the growth rate for polycrystalline cubic boron monophosphide (BP) on alumina substrates versus the reciprocal absolute temperature.. The PBr3 pressure
The results obtained in the present investigation vere compared to those obtained by other investigators (Fitzer, van den Brekel, Bossignol) and their respective
In the next sections, a few examples of diamond deposition these materials are given. In the case of diamond deposition on graphite substrates, the growth conditions induce
In situ volume mixing ratios (VMRs) of N 2 O measured by the SPIRALE instrument on 2 October 2002 at mid-latitudes (black line) and compared to the VMRs simulated by the Reprobus