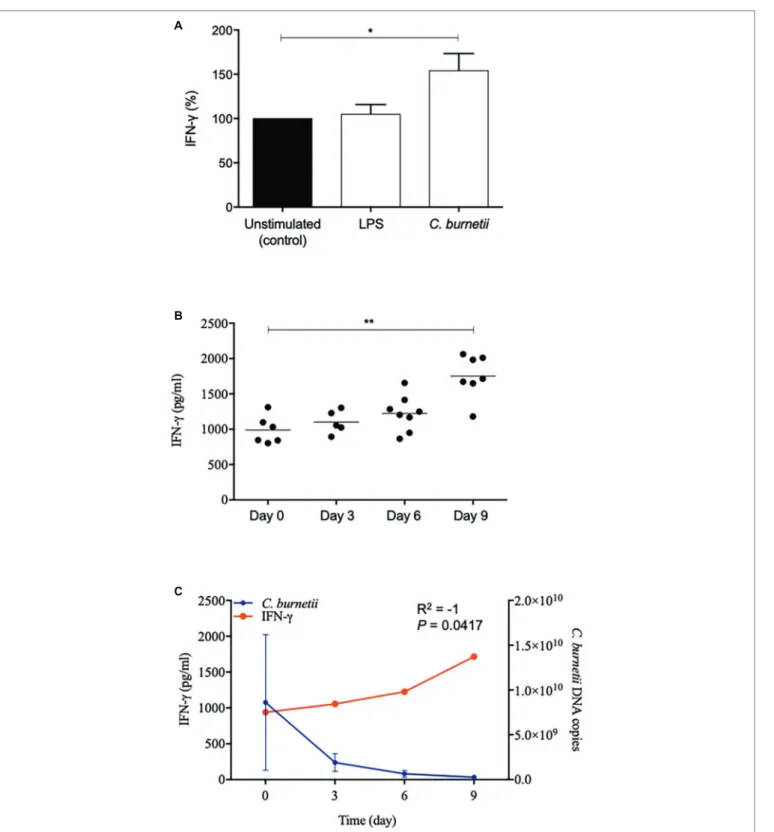
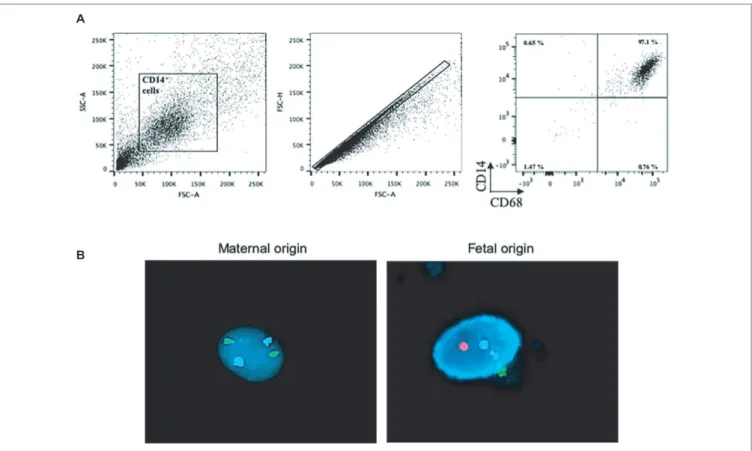
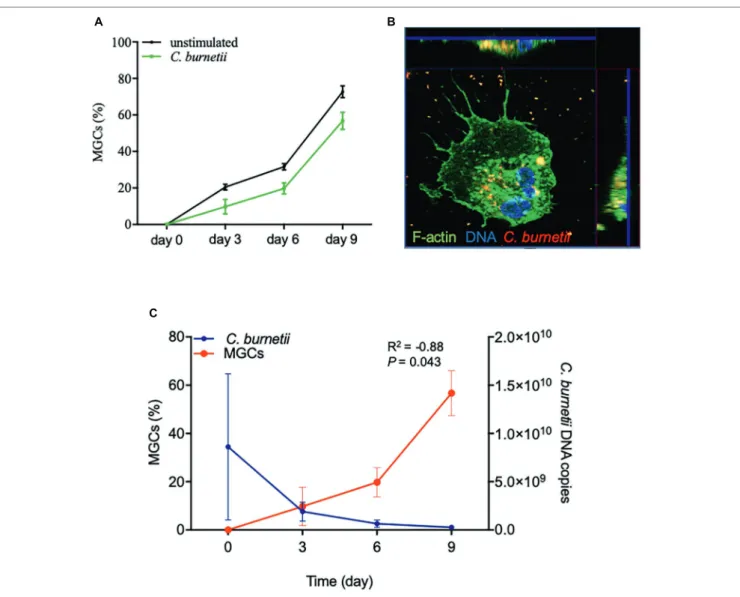
Full-Term Human Placental Macrophages Eliminate Coxiella burnetii Through an IFN-γ Autocrine Loop
Texte intégral
Figure


Documents relatifs
Aucune différence significative n’est constatée entre les mesures répétées du volume du modèle en acrylique : entre la première et la deuxième série de
Fetal gonads Utero-placental unit Utero-placental unit Mare Mare P5 17αOH Pregnenolone Dehydroepiandrost erone (DHEA) 7-dehydro DHEA Androstendio ne Testoster one Oestrone
We identified some SNPs in clock- related genes (e.g., rs2899663 in the RORA gene) in the placental genome that are associ- ated with placental abruption risk, and these
secreted by B and T cells, dendritic cells and macrophages present in lung tissues. However, since TNF- and IL-10 are typically produced in 477. response to
Analysis of cytokine secretion and transcript expression of SLA stimulated CD8 + T cells showed also a significantly higher IFN-c production in HCL volunteers compared to the
screening against the intracellular form of the parasite [12]. We investigated different time points in the growth curve of the THP-1 cells and Leishmania parasites to determine
We then verified the specificity of the contextualized macrophage interactome composed of 30,182 interactions by showing that it is enriched in proteins related to the immune
Our aim was to develop a method of co-culture using human term placenta, to be close to in vivo placental barrier, including mesenchyme and trophoblastic cells, in a