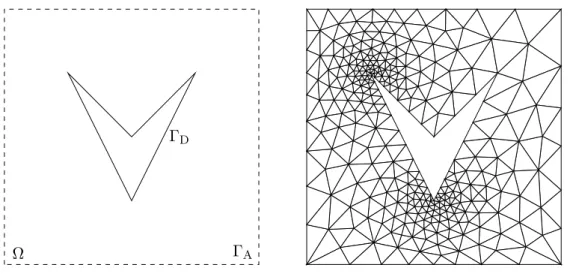
On the derivation of guaranteed and p-robust a posteriori error estimates for the Helmholtz equation
Texte intégral
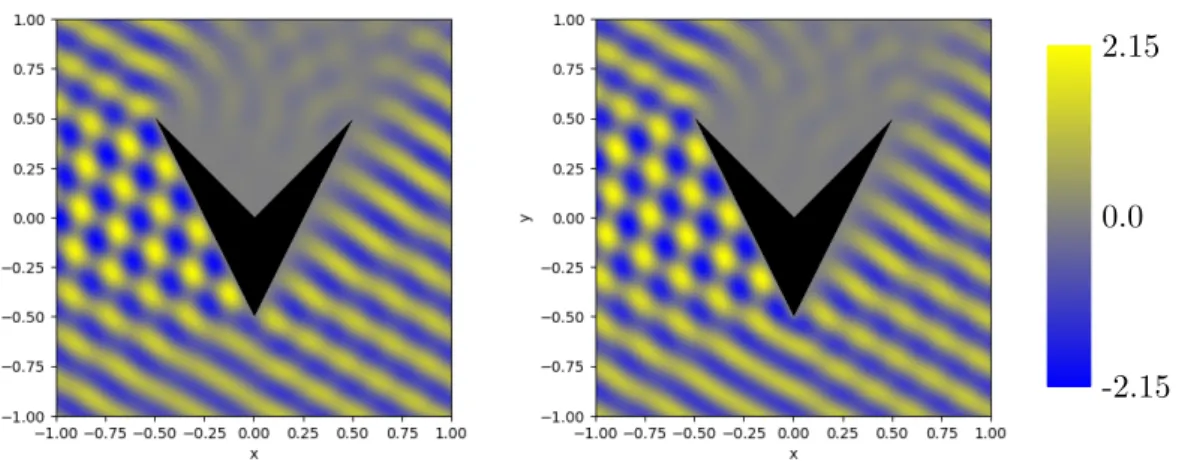
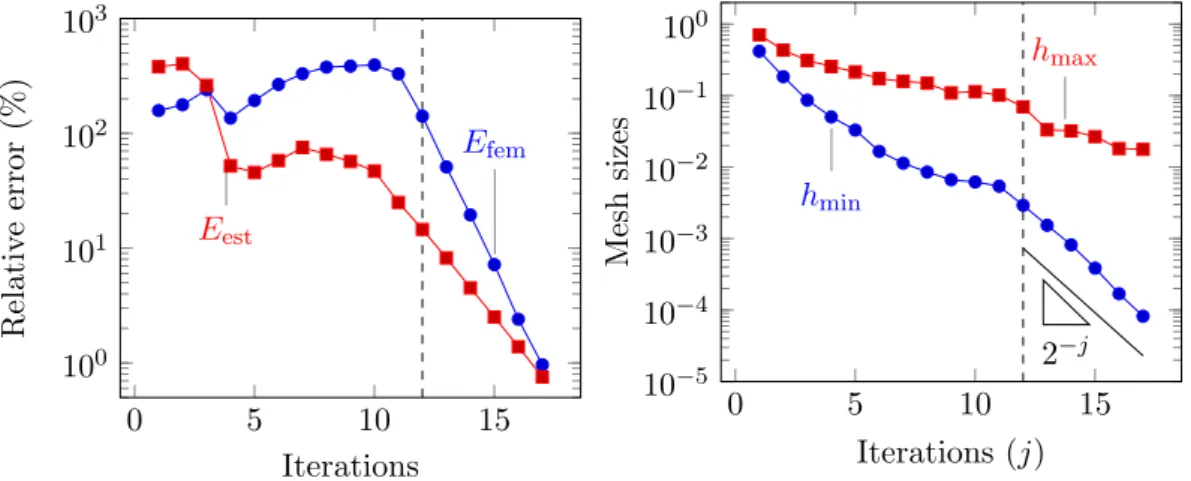
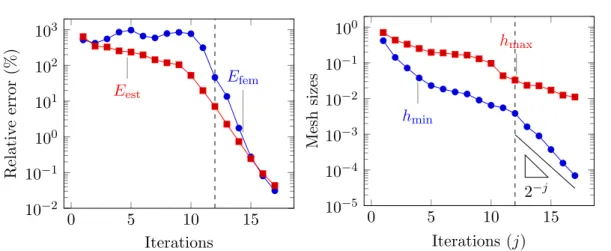
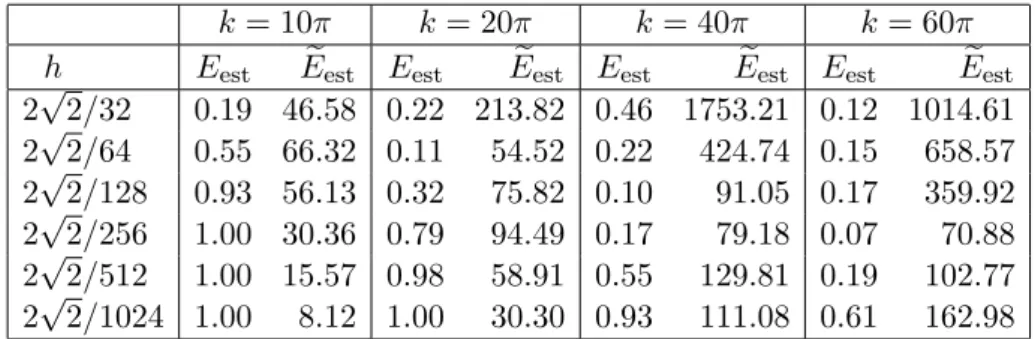
Figure


Documents relatifs
C´ ea’s lemma plays an important role in finite element theory, since it enables us to transform the question of convergence of the finite element method (and a priori estimation for
The Ultra Weak Variational Formulation (UWVF) of the Helmholtz equation provides a variational framework suitable for discretization using plane wave solutions of an appropriate
To deal with these situations, we propose robust a posteriori error estimates for the heat equation with discontinuous, piecewise constant coefficients based on a discretization
A method has been presented to recover lower and upper bounds for the computation of a reliability index in a finite element reliability analysis.. This method is based on
Polynomial robust stability analysis for H(div)-conforming finite elements for the Stokes equations. Elliptic reconstruction and a posteriori error estimates for parabolic
In Farhloul and Manouzi [1], these authors have introduced a mixed finite el- ement method for problem (0.1) based on the introduction of σ = |∇ u | p − 2 ∇ u as a new unknown and
Crouzeix-Raviart element, nonconforming method, stabilized method, nonlocking, a posteriori error estimates.. AMS
We propose a new robust a posteriori error estimator based on H (div ) con- forming finite elements and equilibrated fluxes.. It is shown that this estimator gives rise to an