Domain decomposition methods to model heat exchanges between a well and a rock mass
Texte intégral
Figure

![Figure 2: Both |G RR (k)| and |G DN (k)| (top) and 1 − |G DN (k)| (bottom) as a function of k ∈ [0, k max ] obtained with Q n = 30000 nm 3 .h −1 , ∆t = 6 h and with β ff = h, β rock = DtN [ rock (0), θ given by (16)](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/13539837.418498/13.892.136.767.131.365/figure-rr-function-obtained-rock-dtn-rock-given.webp)
![Figure 4: |G RR (k)| as a function of k ∈ [0, k max ] obtained with the Robin coefficients given by a numerical approximation of the min-max problem, by the choice β rock = DtN [ rock (0), β ff = h (denoted DtN0-h) and by the choice β rock = DtN [ rock (0)](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/13539837.418498/14.892.125.766.128.579/figure-function-obtained-coefficients-numerical-approximation-problem-denoted.webp)
![Figure 5: Convergence rate (defined as the maximum of |G RR (k)| in k ∈ [0, k max ]) as a function of the normal flow rate Q n for the Robin coefficients obtained by a numerical approximation of the min-max problem (min-max), by the choice β rock = DtN [ r](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/13539837.418498/15.892.239.657.132.426/figure-convergence-defined-function-coefficients-obtained-numerical-approximation.webp)
Documents relatifs
Since the test case considered here is symmetric with respect to the axis r = 0, system (48) is written in axi-symmetric formulation. The overall scheme is based on a fractional
Test Case 1 concerns the estimation of an optimal time-dependent heat flux q(t) that makes possible the simultaneous estimation of all Luikov’s parameters of cer- amics from a
The computed distributions with direct numerical simulation of plasma velocity and temperature for case of inlet gas velocity at x- y-plane of z = 0 are shown in figs. Similar
Chapter 2 2.1 Capillary Pressure in Passive Heat Transfer devices
The index used to compare different HP working fluids for comparable applications is named figure of merit and an more it is larger, more efficient is the binomial
Our estimates yield a guaranteed and fully computable upper bound on the error measured in the space-time energy norm of [19, 20], at each iteration of the space-time DD
Key words: two-phase Darcy flow, discontinuous capillary pressure, finite volume scheme, domain de- composition method, optimized Schwarz waveform relaxation, Robin and
Key words: Two-phase Darcy flow, discontinuous capillary pressure, finite volume scheme, space–time domain decomposition method, optimized Schwarz waveform relaxation, nonlinear

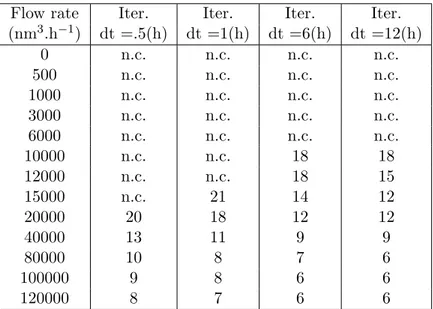

![Figure 7: Convergence of the DDM residual (23) with one curve for each time step as a function of the cumulative number of DDM iterations for the 3D radial test case with random thermal conductivity λ rock ∈ [2, 5] W.K −1 .m −1 on the mesh 50 × 50 × 200 wi](https://thumb-eu.123doks.com/thumbv2/123doknet/13539837.418498/22.892.131.765.128.355/figure-convergence-residual-function-cumulative-iterations-thermal-conductivity.webp)

