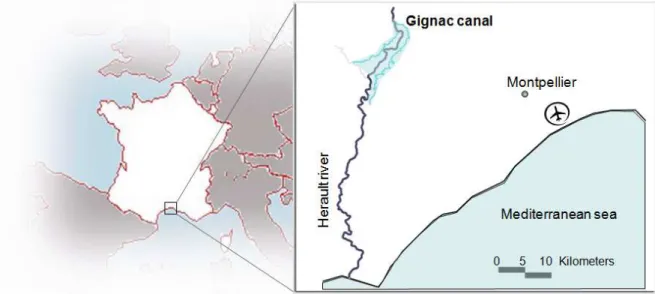
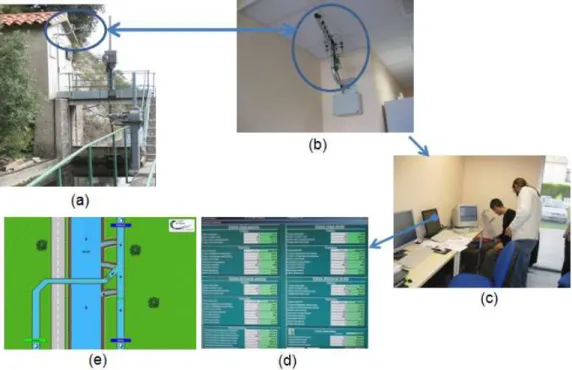
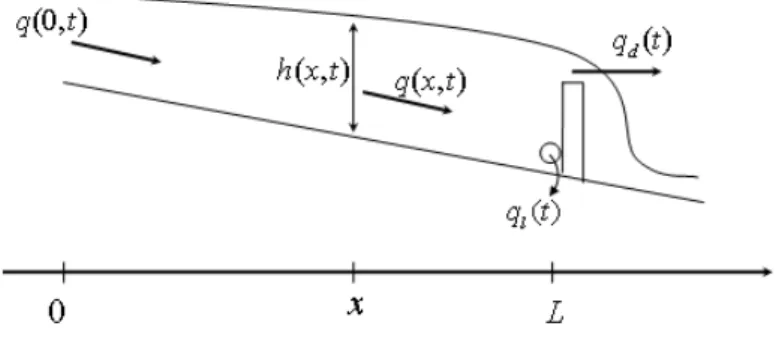
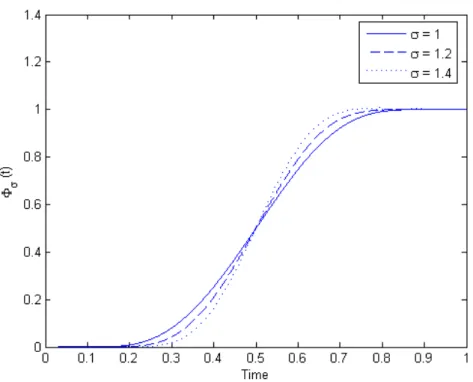
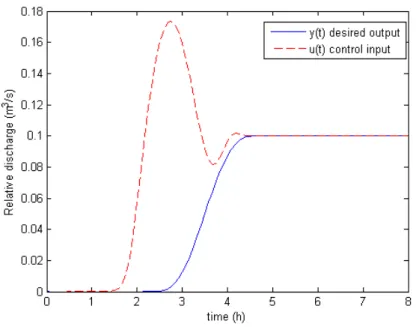
Flatness-based control of open-channel flow in an irrigation canal using SCADA
Texte intégral
Figure

Documents relatifs
To tackle this, a case study on Kenya presents (failed) re-forms such as universal or categorical free health care or the introduction of health insurance and the expansion of its
A preliminary analysis of the data recorded in the experiment stressed out the necessity to distinguish the different types of passages: normal driving without any
The present study aims to evaluate the economic distortion in trade metrology due to metrological frauds in measuring instruments used in the commerce
As the paper focuses on the transitions between the different flow patterns, the strategy employed is to keep a constant mean flow (water depth and mean
The main idea is to relate, in a certain limit, Gibbs states of large bosonic systems to non-linear Gibbs measures built on the associated mean-field functionals.. This is
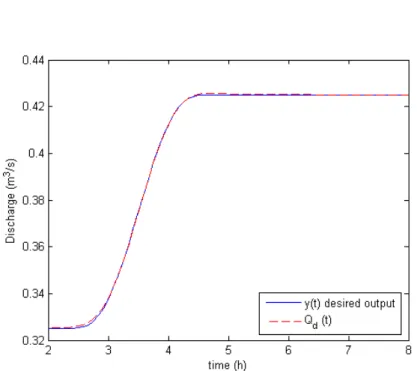
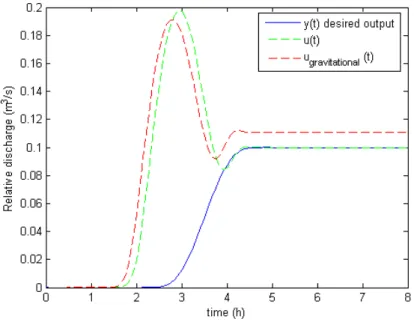
Then the global stability (observer + controller) is checked using theorem 5. The maximum numbers of packets lost for the two modes are 0 and 3 respectively while the system
(a) Reynolds number variation (control laws were designed for Re = 100), (b) Amplitude of the inflow perturbations divided by their nominal value, (c) Amplitude of the
The robustness of the control law was evaluated considering Reynolds, mean flow velocity, amplitude of the inflow perturbations and perturbations inserted between input and