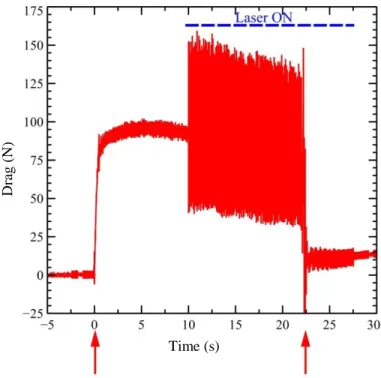
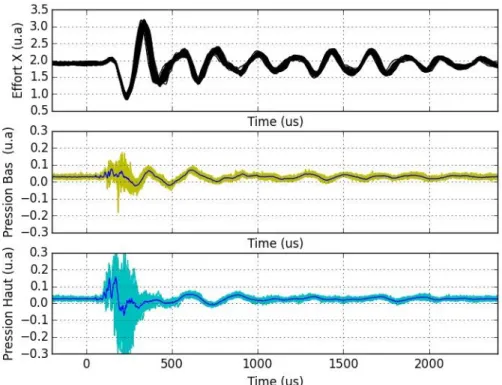
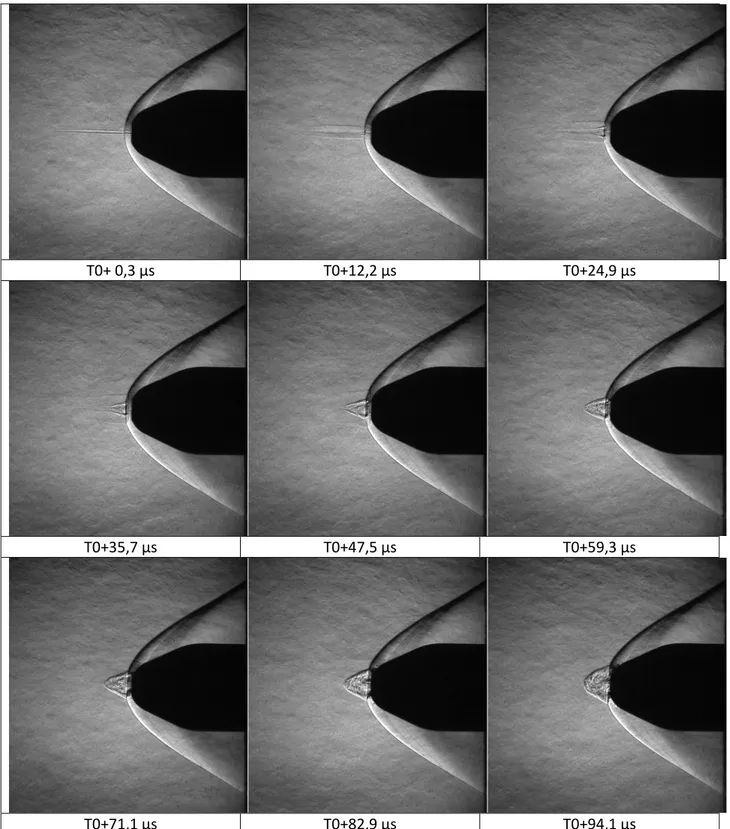
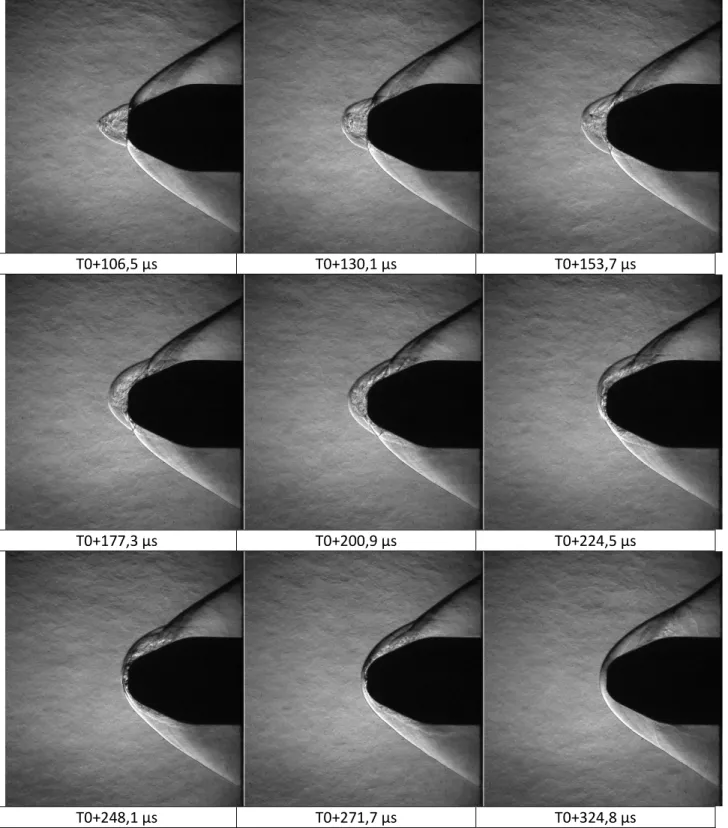
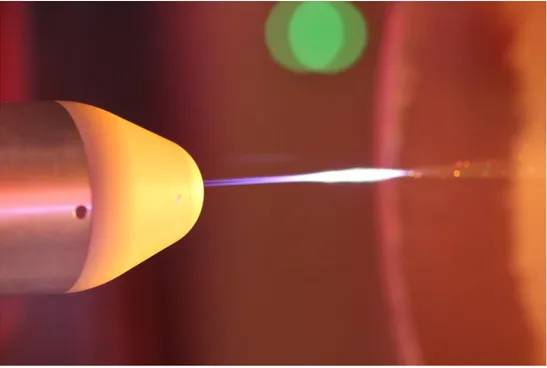
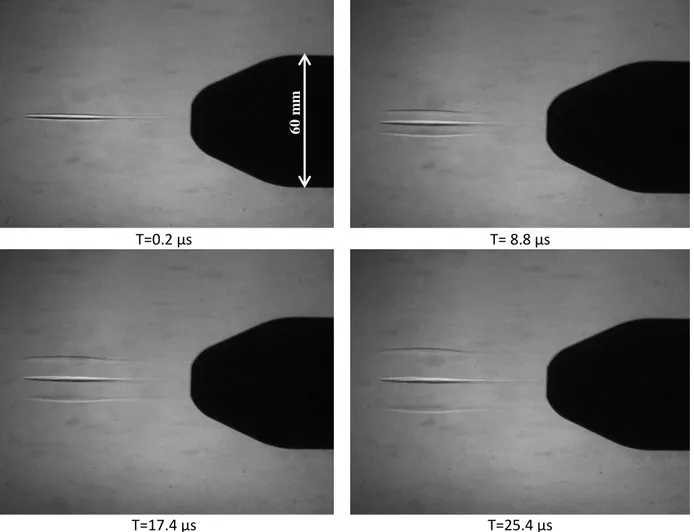
Experimental Investigation of Linear Energy Deposition Using Femtosecond Laser Filamentation in a M=3 Supersonic Flow
Texte intégral
Figure
Documents relatifs
PCM pictures of single short pulse irradiation effects in fused silica and BK7 glass at different pulse energies (E). The laser propagates along z. For both glasses, the
We have investigated the deposition of metallic (copper, aluminium, tantalum, nickel) nanoparticles by femtosecond pulsed laser ablation.. The experimental arrangement is the same
Two series of experiments were done, one at constant flow, the other one at constant current, The essential data and measurements of the temperature, electronic density and reduced
Using a plasma chemistry containing a fl uorinated silicon precursor (SiF 4 ), no deposition is ob- served on an aluminum oxide (AlO X ) surface area, whereas a thin fi lm of silicon
The numerical simulations are divided into three stages discriminated by the duration of the process: (i) non- linear propagation of the beam and laser pulse energy deposition
Xu, " Long lifetime plasma channel in air generated by multiple femtosecond laser pulses and an external electrical field," Opt.. Durnin, "Continuously self-imaging
Delete Four key factors for the single pass lasing from filaments can be identified, namely the incident seed pulse energy, the density of population inversion, the
The initial stage of laser energy de- position consists in the generation of a localized weakly ionized plasma with typical density of one electron per hundreds of molecules in