Optimal location of resources maximizing the total population size in logistic models
Texte intégral
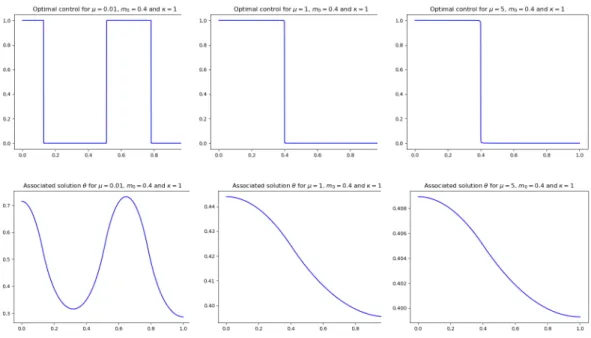
Figure

Documents relatifs
By assuming the diffusion rate of the species large enough, we prove that any optimal configuration is bang-bang (in other words an extreme point of the admissible set) meaning that
Thus the handling and the storing of mobile resources, such as containers, will create imbalances in the logistics network, leading to starvation or overstocking of
In this paper, we consider a spatiotemporal growth model where a social planner chooses the optimal location of economic activity across space by maximization of a
Second we are able to identify a much stronger asymmetry between the Benthamite and Millian cases: in our AN setting with finite lives, the Millian case systematically leads to
Abstract. We first recall some basic facts from the theory of discrete-time Markov chains arising from two types neutral and non-neutral evolution models of population genetics
After a description of population-based and tourism employment in France and its distribution in terms of density across functional economic areas, this section
First, the mixture of logistic regression model is presented in Section 2.1, and the prediction step is described thereby. Then, parameter estimation by maximization of the
In the simpler case where no advection term was included in the population dynamics equation, a fine study of the optimal design problem [15, 19] allowed to emphasize