A finite volume scheme for convection-diffusion equations with nonlinear diffusion derived from the Scharfetter-Gummel scheme
Texte intégral
Figure
Documents relatifs
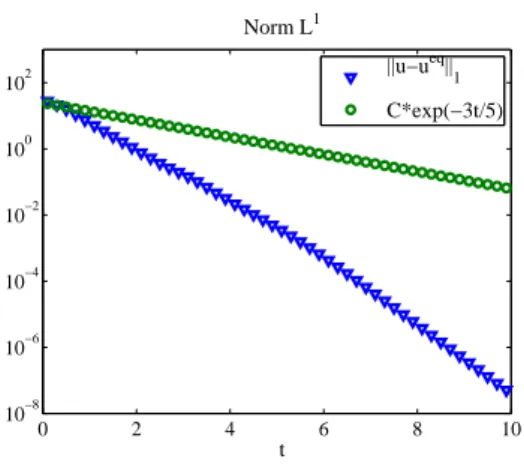
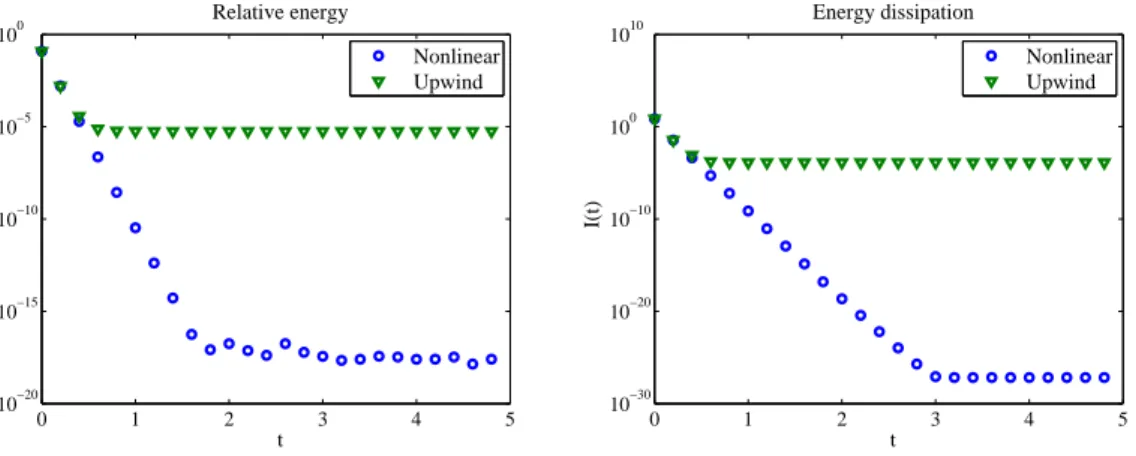
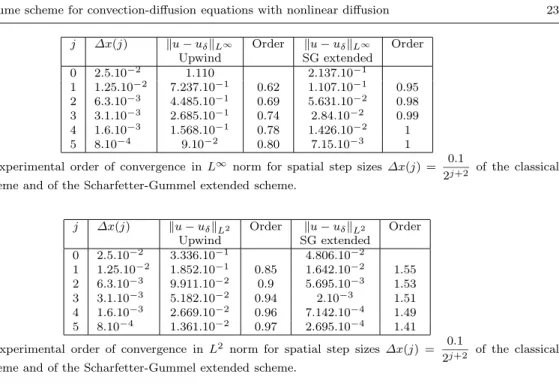
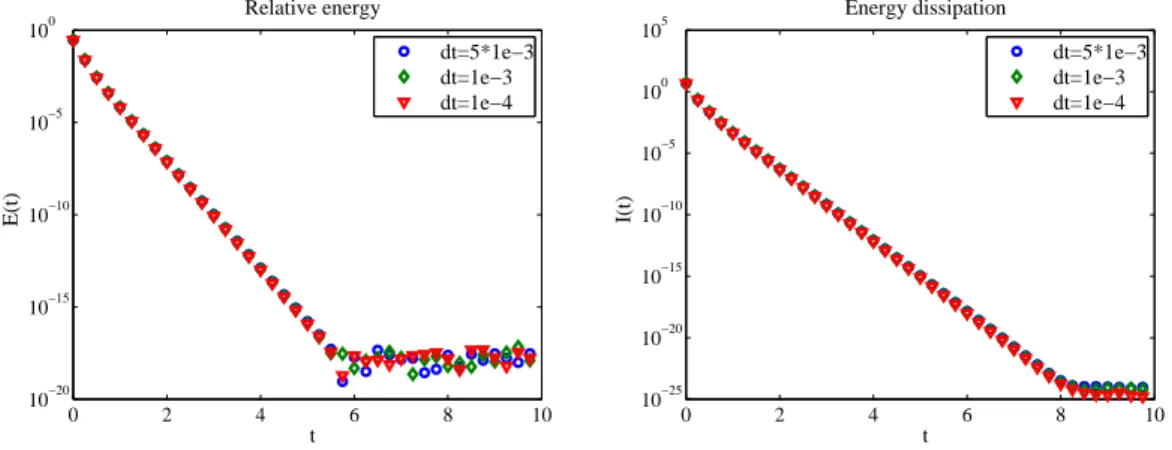
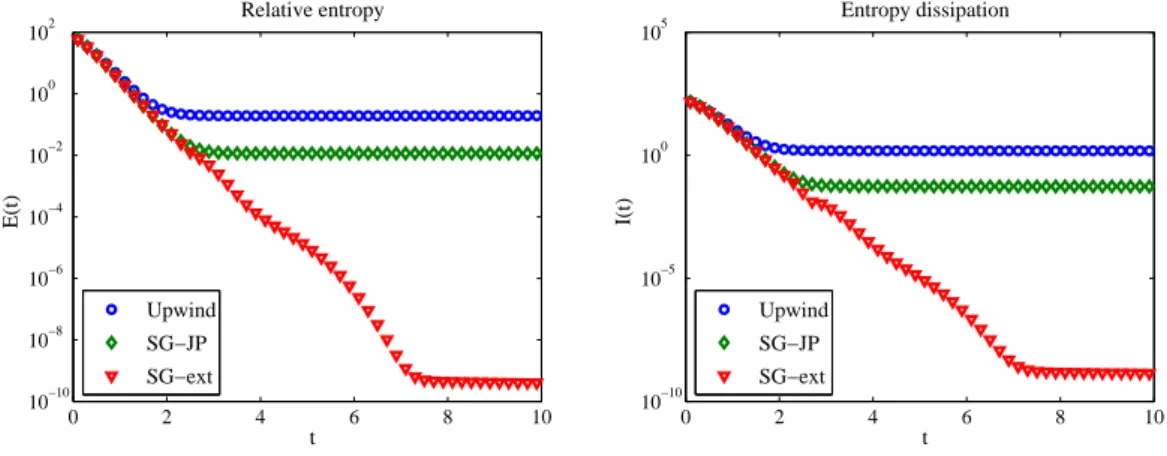
After proving well-posedness, stability, exponential return to equilibrium and convergence, we gave several test cases that confirm the satisfying long time behavior of the
We present a new very high-order finite volume scheme for the two-dimensional convection-diffusion problem system based on the local Polynomial Reconstruction
Then we show the convergence of a sequence of discrete solutions obtained with more and more refined discretiza- tions, possibly up to the extraction of a subsequence, to a
While almost all the schemes mentioned before are based on very similar ideas, the approach proposed in [23] has been shown to be very general, since it applies to kinetic equations
Key words: degenerate parabolic problem, convection–diffusion–reaction equation, inhomoge- neous and anisotropic diffusion, convection dominance, nonmatching grids, finite
Wellknown discretization methods are finite differences, finite volumes and finite elements. The mathemat- ical study of convergence is quite wellknown in the case of
We present a fourth-order in space, second-order in time finite volume scheme for transient convection diffusion problem based on the Polynomial Reconstruction Operator and
As far as non- local equations are concerned, continuous dependence estimates for fully nonlinear integro-PDEs have already been derived in [38] in the context of viscosity solutions