Selenoproteins and Protection against Oxidative Stress: Selenoprotein N as a Novel Player at the Crossroads of Redox Signaling and Calcium Homeostasis
Texte intégral
Figure

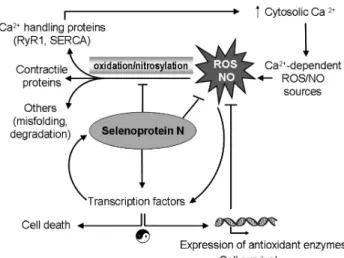
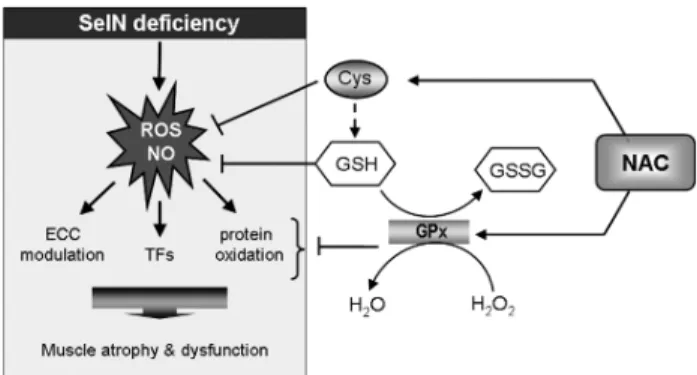
Documents relatifs
We describe the particle motion in a vertical tube of the same diameter as those used in a solar receiver, investigated through the use of the Positron Emission Particle Tracking
Particle in cell simulations were carried out with a plasma bounded by two absorbing walls and a magnetic field applied parallel to them. Both the sheath extent and the potential
In addition, this voluntary wheel running protocol decreased brain disorders (BBB leakage and macrophage accumulation) and aortic plaque size, and increased aortic
To induce basidiomata production, we with- drew water for 15-20 days (water stress). Six phases of fungal development on the cookies were studied: 1) white phase, corresponding to
The oxidative stress linked to inflammation plays an important role in (i) endothelial dysfunction, with reduced nitric oxide (NO) bioavailability, (ii)
gene expression and modulates fermentation product formation and oxidative stress
On a dry mass basis sun exposed leaves of seedlings and adult canopy trees displayed significantly higher amounts of total ascorbate and a-tocopherol (figure 1) and lower
Regarding the expression of anti-inflammatory genes, AO supplementation had a specific effect, by inducing both IL-4 and IL-10 mRNA levels in AO + LPS mice, while OO supplementation