Functional renormalisation group in a finite volume
Texte intégral
Figure


Documents relatifs
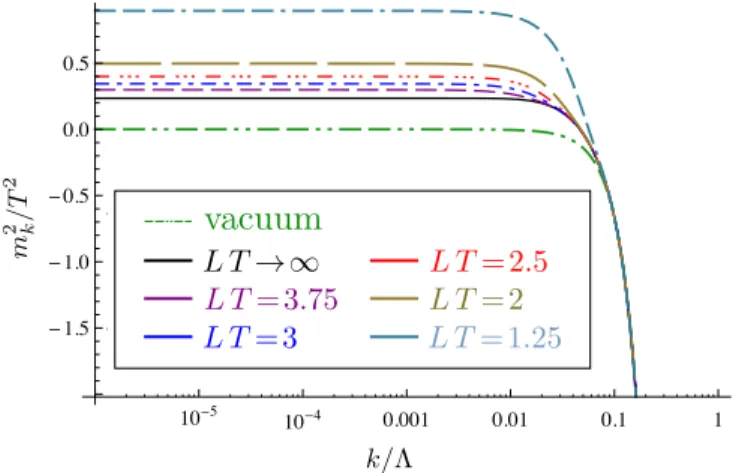
The thermal behavior of the or- der parameter, the susceptibility, and its derivative with respect to temperature, is investigated, as well as that of the …rst four cumulants of
Let us consider the case where we only deal with scalar particles in the initial and final state or we sum and average over all possible polarization of non scalar particles..
L’accès aux archives de la revue « Rendiconti del Seminario Matematico della Università di Padova » ( http://rendiconti.math.unipd.it/ ) implique l’accord avec les
Keywords: Gyrokinetic limit; Finite Larmor radius approximation; Anisotropic quasineutral limit; Anisotropic hydrodynamic systems; Analytic regularity; Cauchy–Kovalevskaya
• [3] : application to p-divisible groups, construction of Hecke invariant stratifications of the p-adic moduli spaces, fundamental domains for the actions of Hecke correspondences
They referred to the Ans¨ atze (1.1) and (1.2) as “self- preservation hypotheses,” since the shape of the spectrum and correlation function are thereby preserved in the decay
Moreover, the dimension of the projective cover of the simple module associated to the conjugacy class of the p-regular element g ∈ G is equal to the number of conjugacy classes
For problematic cells, the solution is recomputed with a lower-order unlimited scheme (using polynomials with lower degree) and we repeat the procedure detection-degree