Spatially periodic domain wall pinning potentials: Asymmetric pinning and dipolar biasing
Texte intégral
Figure



Documents relatifs
Tectonically active for the past ~160 million years, the igneous basement of the Indian Ocean basin has formed due to complex interactions between mid-ocean ridges and
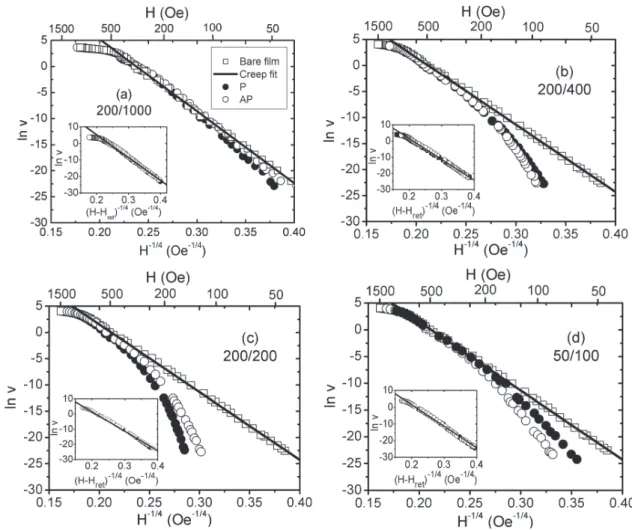
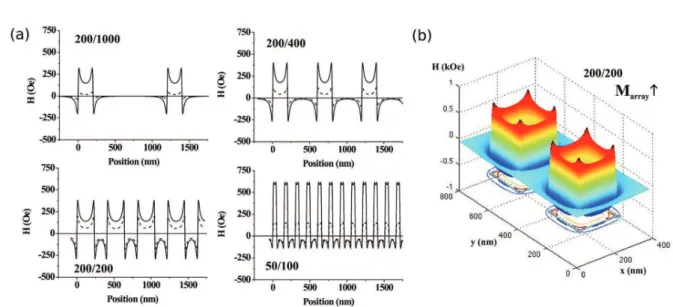
In this work, we have studied DW propagation in patterned Co/Pt multilayers as a function of temperature and geometry in order to find a suitable regime in which the magnetic
(A) Lysates of HEK-293 cells stably expressing recombinant human 11b-HSD2 were incubated for 10 min at 37°C with 50nM of radiolabeled cortisol and increasing concentrations
micro structural ones (grain diameter, density, poro- sity). Samples and experimental procedure. Presintering was done to assure the same specific saturation magnetization for all
L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, émanant des
We study pinning asymptotics numerically, using auto07p and direct simulations.. In particular, we corroborate our results numerically, confirming the value of
We bave recorded trie burst size distribution, g(s), in trie long time regime, considering trie bursts which can be defined at every elementary time step.. Let us consider two
the point interactions between flux lines and pinning points add to determine the pinning force density P. The critical current is then