Draft genome sequence of the male-killing Wolbachia strain wBol1 reveals recent horizontal gene transfers from diverse sources
Texte intégral
Figure

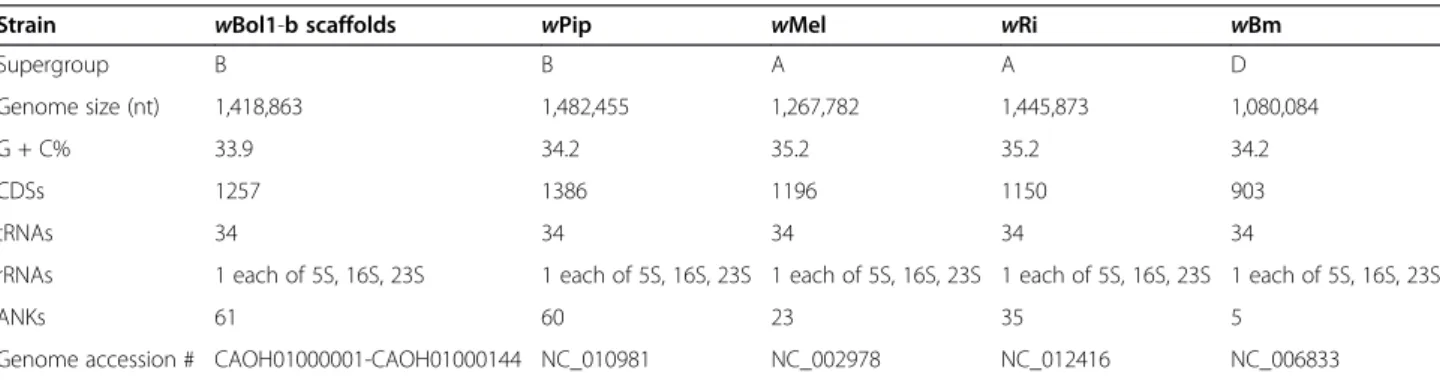

Documents relatifs
By comparing the genomes of ten Penicillium spe- cies, we show that adaptation to cheese was associ- ated with multiple recent horizontal transfers of large genomic regions
Horizontal gene transfer in fungi may be beneficial, particularly in cheese making strains or wine yeasts, in which large transfers of genes promoting fermentation have been detected
Bonnes vacances et j'espère tous vous retrouver à la rentrée en pleine forme, hors de question de laisser entrer un crapaud dans ma classe..
Using network approach in the context of HTT involves defining three characteristics: (1) the network topology, which captures the diversity of organisms potentially involved in HTT
Similarly, the RAST server predicted a total of 5202 features, of which 5125 represent coding se- quences (CDS), 6 rRNA and 71 tRNA genes. The annota- tion derived from the RAST
At low resolution with the grid-spacing dependent horizontal mixing, the wave motion is the same for both coupling modes because the wave deviation by the currents is weakI. In
In this issue of Molecular Autism, Soorya and colleagues evaluated 32 patients with Phelan-McDermid syndrome, caused by either deletion of 22q13.33 or SHANK3 mutations,
Major findings in our study on the knock-out of the excitatory kainate receptor subunit GluK2 were an improved glucose tolerance characterized by reduced glucagon release,