Learning Optimal Decision Trees with MaxSAT and its Integration in AdaBoost
Texte intégral
Figure
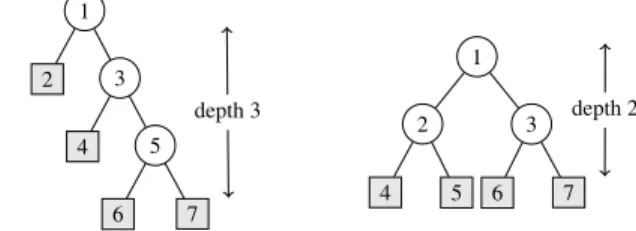
Documents relatifs
cytometree is an unsupervised algorithm for flow cytometry that exhibits better performance in terms of the F -measure than the best unsupervised algorithms, as tested on FlowCAP I
We consider sets of words (sequences of symbols) and their corresponding generating functions to get precise average case analysis (here expected value and variance) of
The join operation is used for the generation of every element of ~’n from binary trees with. less vertices. Indeed
From the results on monotone and left- monotone deterministic RL -automata mentioned above it follows quite easily that each left-to-right regular language is accepted by a
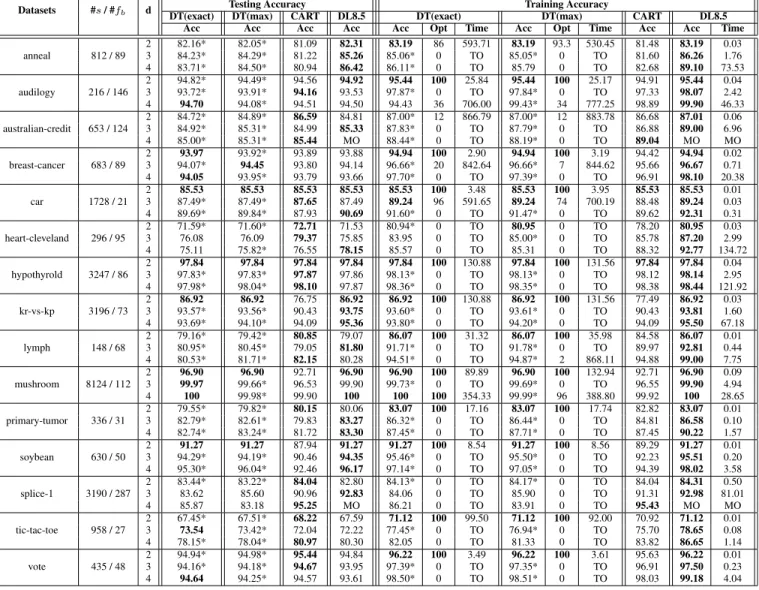
Overall, our encoding requires O(2 K (F +C +log(T max ))) decision variables and O(R +2 K (F ·T all +C)) constraints, where K is the tree depth, F is the number of features, C is
Since there are no binary trees with an even number of vertices, it would perhaps be useful to consider inead binary trees with k leaves (a leaf being a vertex without a
Attendees will observe the behavior of multi-way joins on queries of different selectivity, as well as the impact on total execution time, time for the first answer, and
Dynamic programming (DP) on tree decompositions is a well studied approach for solving hard problems efficiently.. State-of-the-art implementations usually rely on tables for stor-