Syndecan 4 is involved in mediating HCV entry through interaction with lipoviral particle-associated apolipoprotein E
Texte intégral
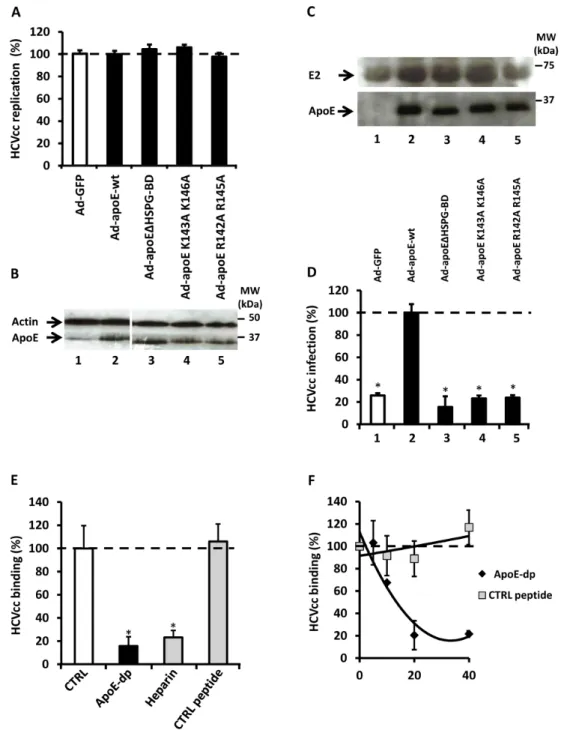
Figure

Documents relatifs
Comme au trimestre précé- dent, cet arrêt de la dégradation de l'emploi total est impulsé par la progression de l'emploi marchand mais s'appuie également sur une dégradation
Patients randomly assigned to group 2 (response-guided therapy) received peginterferon–ribavirin plus bo- ceprevir for a total of 24 weeks after the lead-in period; if HCV RNA
Patients were random- ly assigned to one of four treatment groups: the T12PR24 group, which received telaprevir (VX-950, Vertex Pharmaceuticals), peginterferon alfa-2a
Even though this proves that the linear robust control theory can be applicable to the real system with uncertainties, fixed gain linear controllers cannot always
It is crucial to understand seed traits of these species to develop and implement long-term methods of conservation (i.e., cryopreservation); however, seed tolerance to storage at
Law itz reports receiving consulting fees from AbbVie, Achillion Pharmaceuticals, Idenix Pharmaceuticals, Janssen Pharmaceuticals, Novartis, Merck, Vertex Pharmaceuticals,
Before the development of a cell culture system for HCV (HCVcc) in 2005 [2–4], selectable replicon systems [5] and retrovirus-based pseudotyped particles (HCVpp) [6–8] were major
cytosolic domain required for HCV infection and OCLN cell surface expression. Moreover, it emphasizes the specific involvement of the distal C-terminus domain of