Nonlinear effects in random lasers
Texte intégral
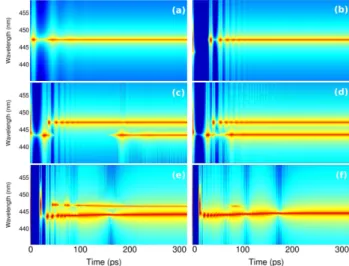
Figure


Documents relatifs
This work presented the study of the nonlinear dynamics of an orchard tower sprayer, coupled with a vehicle suspension, that is subject to random excitations due to soil
By using now this result, Lemma 15 and the Markov property of the random walk and of Brownian motion, we deduce the following:..
In the case of harmonic passive mode-locking, the multipulse generation due to the quantization of the intracavity lasing radiation into individual identical solitons is
Our investigation treats the average number of transversals of fixed size, the size of a random transversal as well as the probability that a random subset of the vertex set of a
We say that a specific pattern M occurs in a tree T if M occurs in T as an induced subtree in the sense that the node degrees for the internal (filled) nodes in the pattern match
- The calculations of the level population of H-like ions made by Bates, Kingston, and McWhirter [6], by McWhirter and Hearn [7] and also in later papers [8, 91
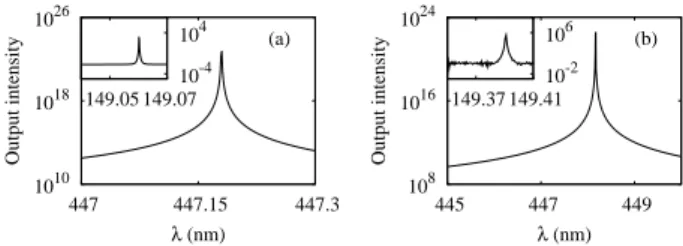
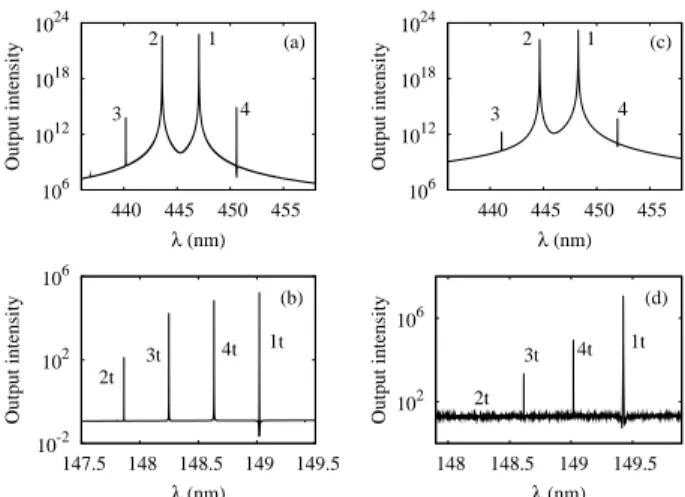
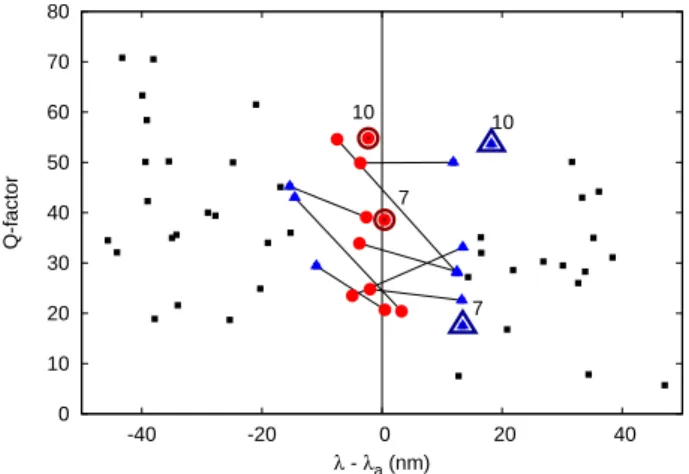
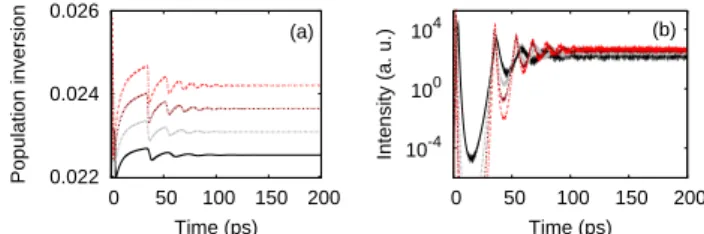
The right-hand sides of the rate equations 共4兲 and 共7兲 contain a first term that corresponds to a competition between photon gain and loss mechanisms, a second term that takes
In order to quantify variability of the responses of mechanical systems which are of interest in engineering applications, several recent works have been applying techniques