The relationship between trade credit, bank credit and financial structure : from firm-level non-linearities to financial development heterogeneity. A study on MENA firm-level data
Texte intégral
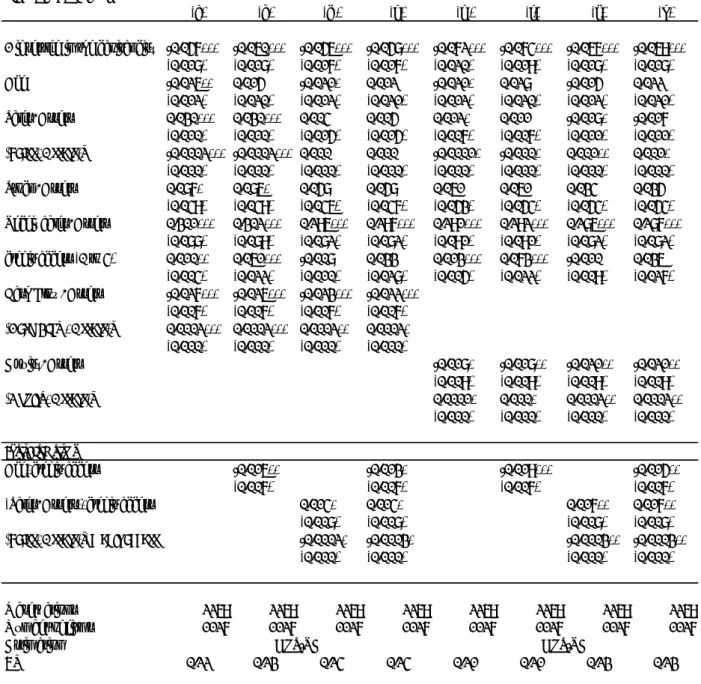
Figure




Documents relatifs
Variation temporelle de la demande biochimique en oxygène (DBO5) des eaux de la station d’épuration entre l’entrée et la sortie pendant la période de suivi.. Variation temporelle
Indeed, the intervener does not benefit from a privileged trading relationship with target countries, and diplomatic intervention affects the trade flows of the target
Cette moyenne , avec un écart type de 0.92, Indique la dispersion des réponses de l'échantillon et veut dire que les pluparts des individus de notre échantillon d’étude
From a panel of 156 Senegalese MFIs, we have created a fixed-effects model to help explain the influence of key variables (MFI size, profitability, risk, etc.) on an MFI's ability
These results indicate that short-term credit is beneficial for growth of small and young firms, contrary to the provision of long-term bank loans.. This finding can be explained by
7 Indeed an increase in the size of Islamic finance reduces the likelihood that a firm was credit constrained in countries with a level of conventional banking development below
Abstract: We use a disequilibrium model to estimate credit rationing to Small and Medium- sized Enterprises on the Tunisian bank credit market.. Based on a panel dataset of 1,275 SMEs
The second robustness checks use Generalized Least Squares (GLS) in the following table 8. The GLS allow to violate OLS assumptions on homoskedasticity or uncorrelated errors.