SNP mining in C. clementina BAC end sequences; transferability in the Citrus genus (Rutaceae), phylogenetic inferences and perspectives for genetic mapping
Texte intégral
Figure
Documents relatifs
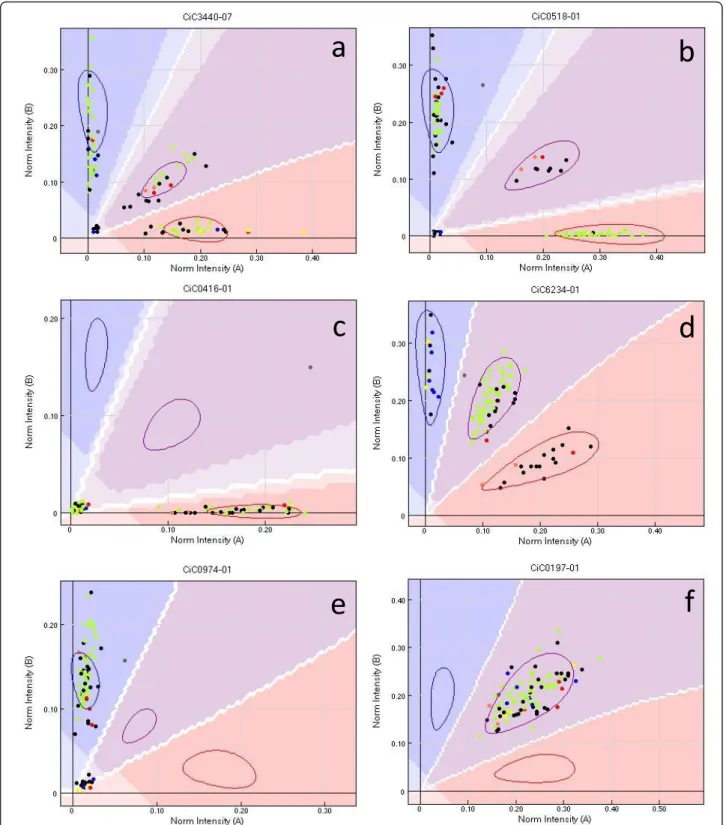
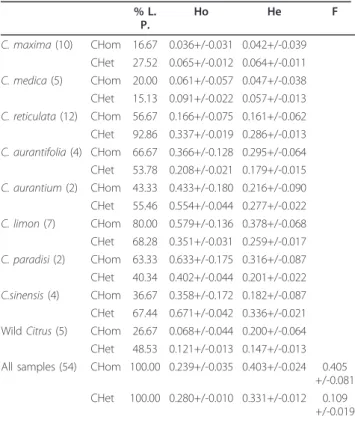
Intra and interspecific polymorphism was observed, and heterozygous markers were identified for the different genotypes to be used for genetic mapping. These results indicate
In order to estimate the rate of mappable EST-SSR markers in each putative F1 progeny we have considered the percentage of Polymorphism of the trinucleotide microsatellite (EST164
Plan defined by the first two axes of a Principal Component Analysis performed on data obtained on 141 clones, representing populations from Peru, Colombia
Evaluation and use of the genetic diversity present in the International Cocoa Genebank ( ICG,T) in Trinidad.. The informations obtained from this assessment are used for
The objectives of the work presented here are (1) to use SNPs previously identified in maize to develop a first reliable and standardized large scale SNP genotyping array; (2)
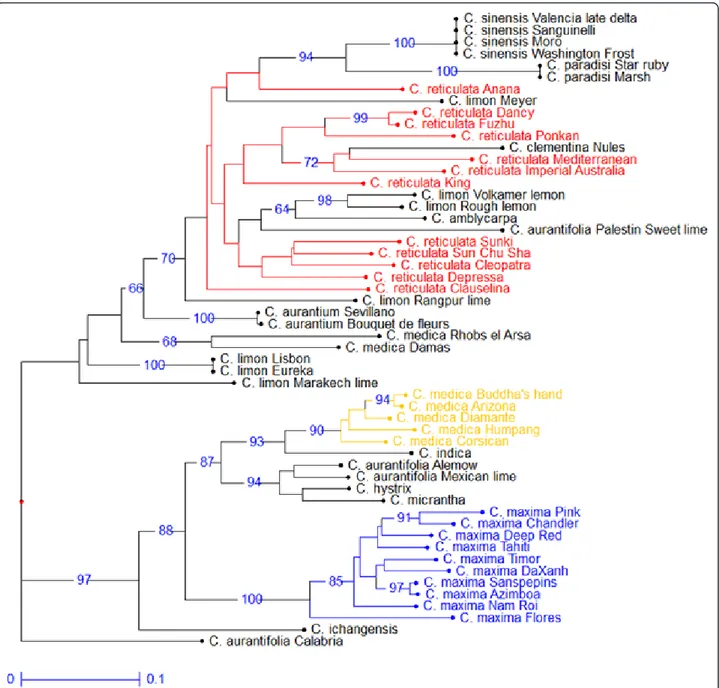
A medium density reference map (961 markers for 1084.1 cM) of clementine was established and used by the ICGC to facilitate the chromosome assembly of the haploid genome
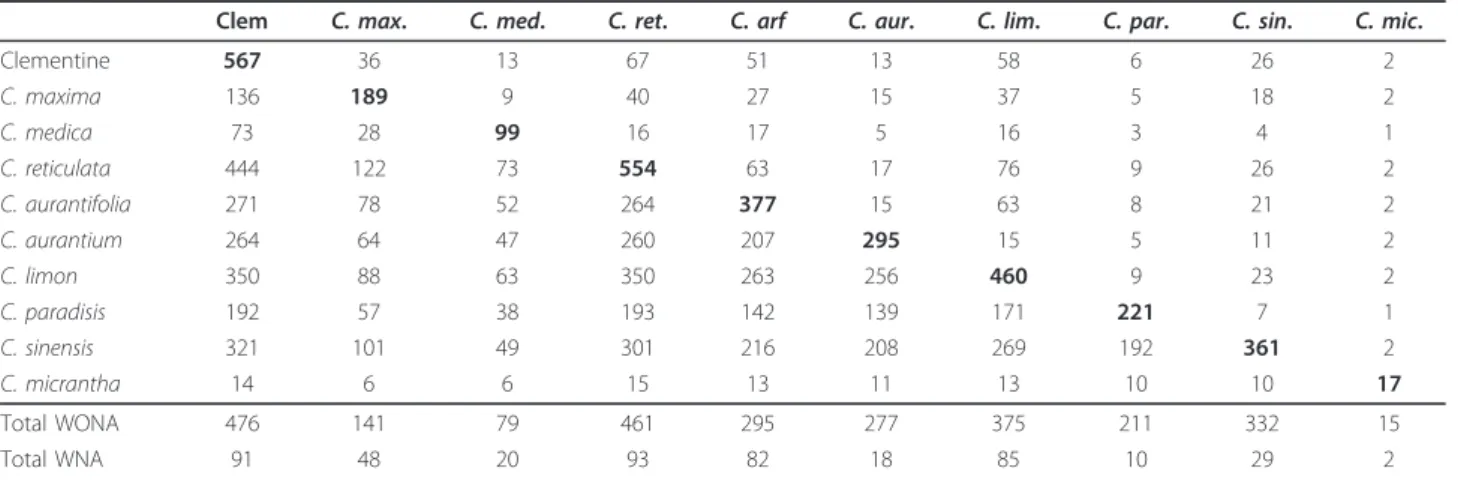
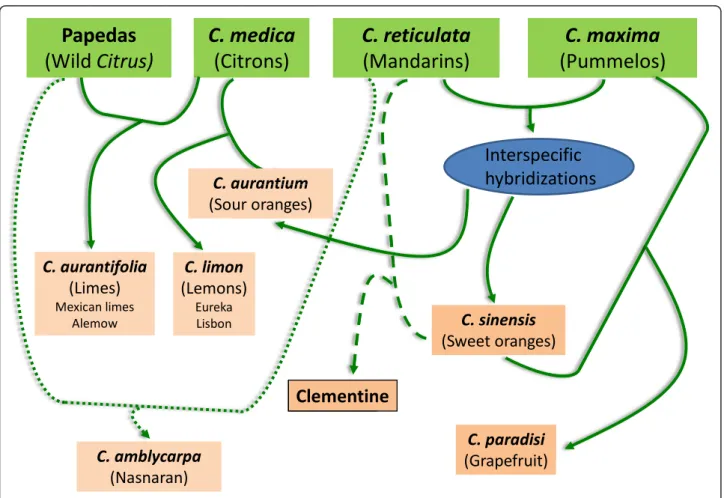
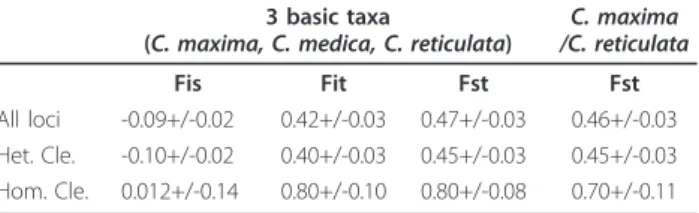
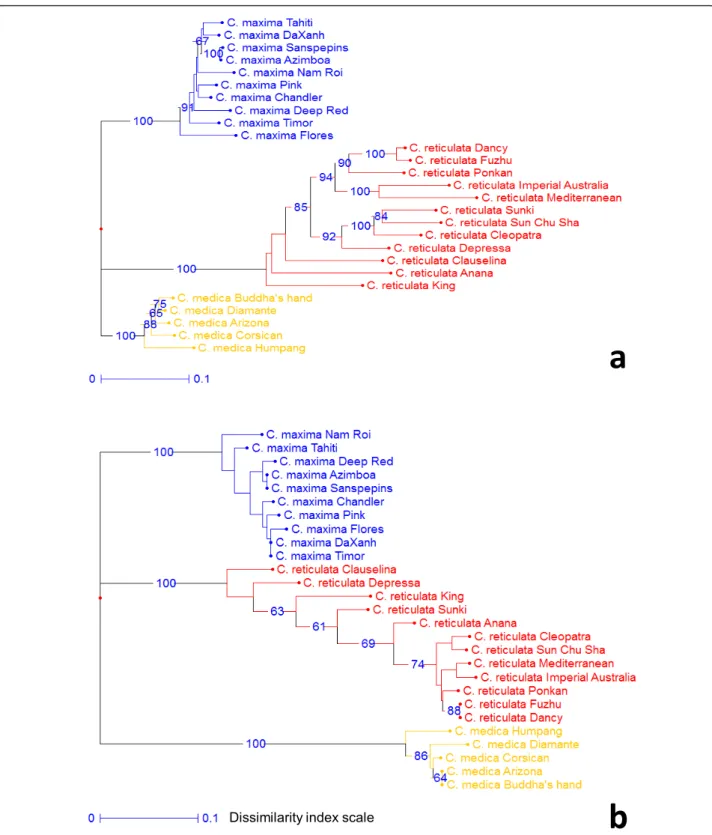
Therefore, SNP markers based on the KASPar method developed from sequence data of a limited intrageneric discovery panel provide a valu- able molecular resource for genetic
The primary goals of the present study were: (i) to assess the use by array genotyping and the transferability of SNPs discovered from the heterozygous Clementine genome within