LiveWSN: A memory-efficient, energy-efficient, reprogrammable, and fault-tolerant platform for wireless sensor network
Texte intégral
Figure


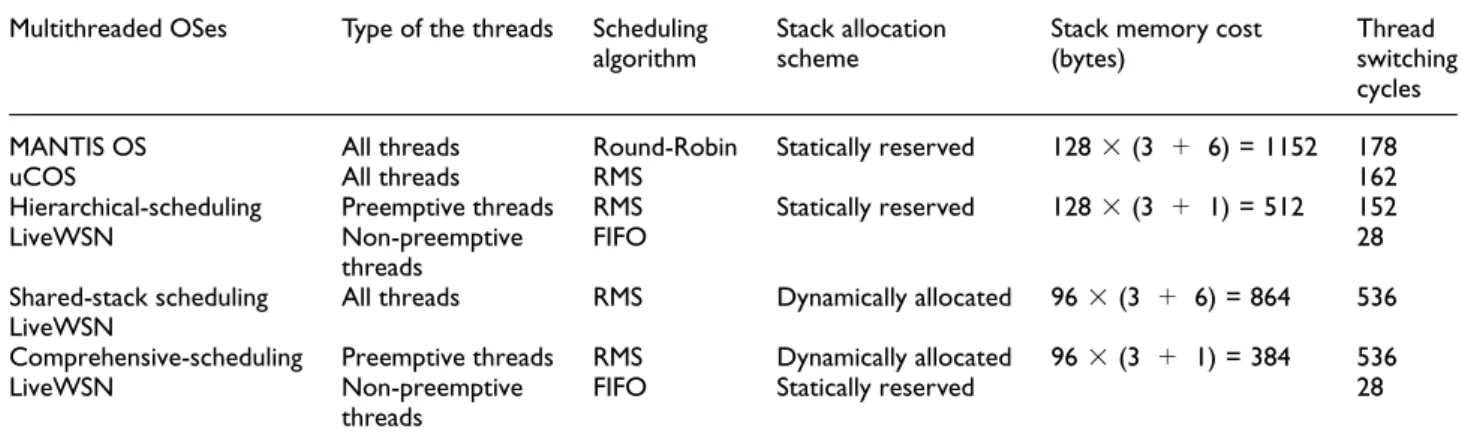
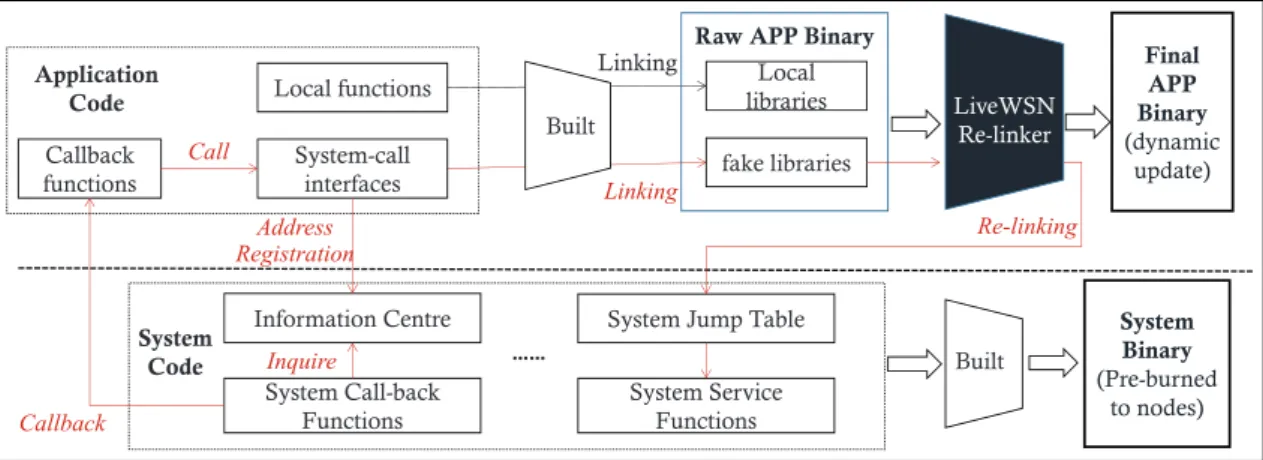
Documents relatifs
While the scheduling community has proposed a large number of static schedulers, i.e., algorithms that take allocation decisions prior to the com- putation based on predicted task
Therefore, for the largest memory bounds, the original graph being itself a valid partial serialization, all the normalized critical paths equal 1. When a method fails to find
This problem is in NP as given a partial serialization of a graph G for a memory bound M, one can check in polynomial time that it is valid: simply compute its maximum peak
The main idea of the new CAFT (Contention-Aware Fault Tolerant) scheduling algorithm is to have each replica of a task communicate to a unique replica of its successors
The DENS methodology minimizes the total energy consumption of a data center by selecting the best-fit computing resources for job execution based on the load level and
The DENS methodology minimizes the total energy con- sumption of a data center by selecting the best-fit comput- ing resources for job execution based on the load level
The numerical results illustrate the energy efficiency of the scheme as a function of the average packet drop probability and the maximum permitted successively dropped

