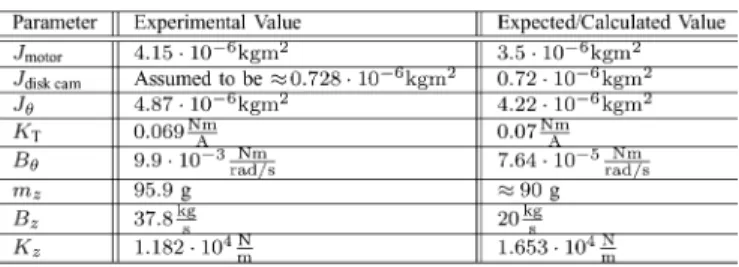
Design and Experimental Implementation of an Electromagnetic Engine Valve Drive
Texte intégral
Figure



Documents relatifs
Abstract The objective of this study was to evaluate the long-term follow-up of patients with Raynaud's phenomenon (RP) and pathological nailfold capilla- roscopy
Pour le délai entre l’accouchement et la sortie de l’hôpital, nous retrouvons la différence d’en- viron 2 jours en moyenne entre un accouchement par voie basse (3,8 jours) et
We use this information in a motion planning based control strategy by, successively, turning the driver’s torque demand into a trajectory generation problem for the air mass
/ La version de cette publication peut être l’une des suivantes : la version prépublication de l’auteur, la version acceptée du manuscrit ou la version de l’éditeur. Access
Figure 1, very roughly derived from discussions with larger builders and prefabricators across Canada, shows that the project builder, using his own central
Ma- ternal Blood Lead Levels and the Risk of Pregnancy-Induced Hypertension: The EDEN Cohort Study.: Lead and Gestational Hypertension.5. Maternal Blood Lead Levels and the Risk
Figure 5 shows 10-day backward tra- jectories calculated from nine grid points around Watukosek at 550 hPa (about 5 km) from the measurement time. A major part of the trajectories
Dans ce travail, on considère une circulation d’air tout autour du bâtiment (sans contact avec l’air intérieur, fig. 1) : a) en hiver fonctionnement en boucle fermée