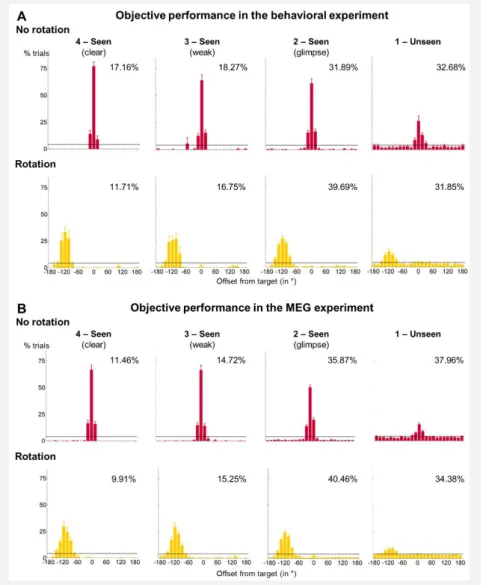
Characterizing the neuro-cognitive architecture of non-conscious working memory
Texte intégral
Figure



Documents relatifs
In Experiment 1b, we manipulated semantic relatedness in immediate serial recall tasks with or without an interfering task by presenting lists of six words that
Support for the mental whiteboard hypothesis 160 Pure working memory account and dual processes account of. number-space associations
Results showed that short-term storage and cognitive control manifested differential links with developing language abilities: Whereas verbal short-term storage was
There is 64 cards in the database, which is corresponds the 4 3 possibilities of values, shapes and colors. We give as inputs to the network a card of the Wisconsin card sorting
(2004) that the cognitive load induced by the processing component within the reading digit span task depends not only on the number of retrievals to be performed and the total
Within the TBRS model, the cognitive load a given task involves corresponds to the proportion of time during which this task captures attention, thus impeding concurrent activities
In the Prose Distraction Task (tapping on access function), depressed patients showed difficulties when attempting to inhibit intrusion of irrelevant words in working memory,
Does a Computer-paced task adjusted to participants capacities reduce strategies and increase prediction of cognitive abilities.. Laboratoire d'Etude de l'Apprentissage et