The rainbow trout genome provides novel insights into evolution after whole-genome duplication in vertebrates.
Texte intégral
Figure

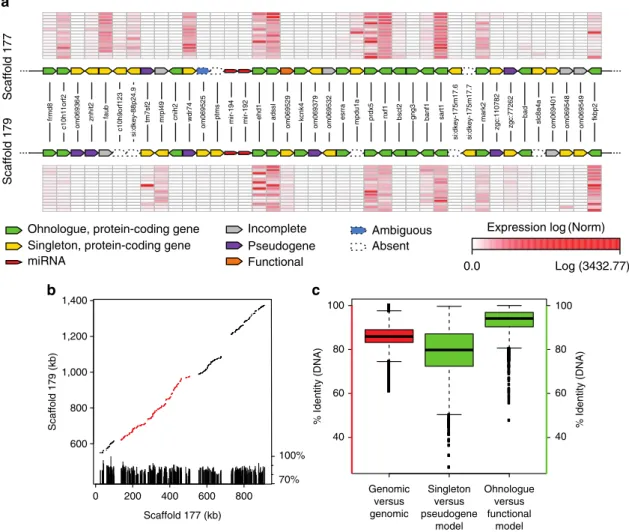
Documents relatifs
Pour ce faire, nous nous sommes appuyés dans un premier temps sur l’observation d’une tâche simple de rotation d’un objet sphérique par le membre supérieur afin de comprendre
L’idée de contrôler l’activité des ribosomes impliqués dans la synthèse des protéines de résistance a été proposée en 2007 comme une stratégie de lutte contre
Major findings in our study on the knock-out of the excitatory kainate receptor subunit GluK2 were an improved glucose tolerance characterized by reduced glucagon release,
In this study, as contributions, we show that MLJS problem can be cast as a MRF model with coupling terms enforcing the consistency between individual seg- mentations and
Of the 128 pigmentation genes analyzed, 46 genes (35.9%) were retained in two copies after the FSGD in at least 1 of the 5 teleost genomes and 65.2% (30/46) of the duplicated genes
fastidiosa (512 = number of orthologs shared only by X. vesicatoria strain 85-10 and S. albilineans strain GPE PC73 conserved in X. maltophilia strain R551-3 and missing in
(1) Cirad, UMR BGPI, Montpellier, France; (2) CEA, Genoscope, Evry, France; (3) Inra, LIPM, Castanet-Tolosan, France; (4) IRD, LGDP, Montpellier, France; (5) Inra, UMR PaVé,
rearrangements: we start with the contracted breakpoint graph of ∆ and Γ, and apply DCJ operations in sequence until all red edges are doubled, which means we reached a doubled