A non-local scalar conservation law describing navigation processes
Texte intégral
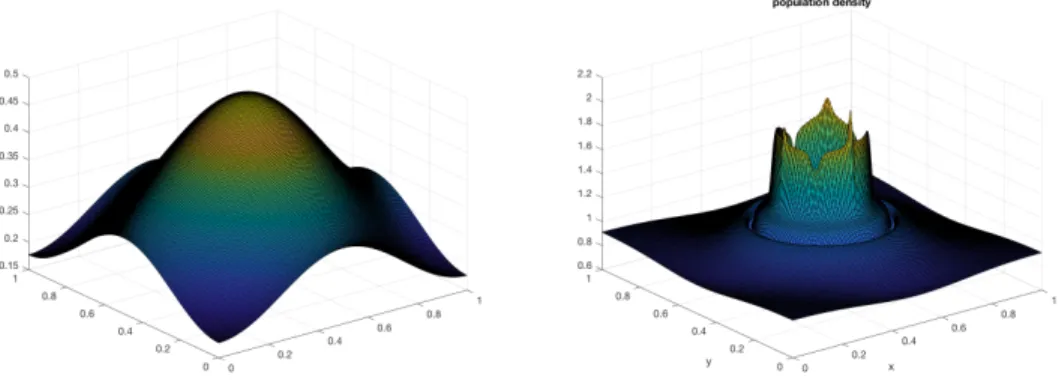
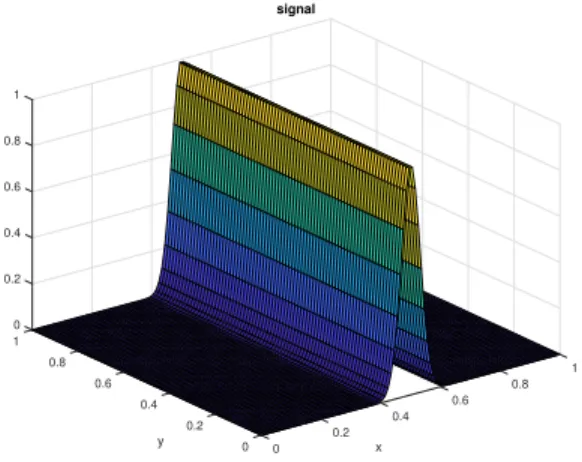
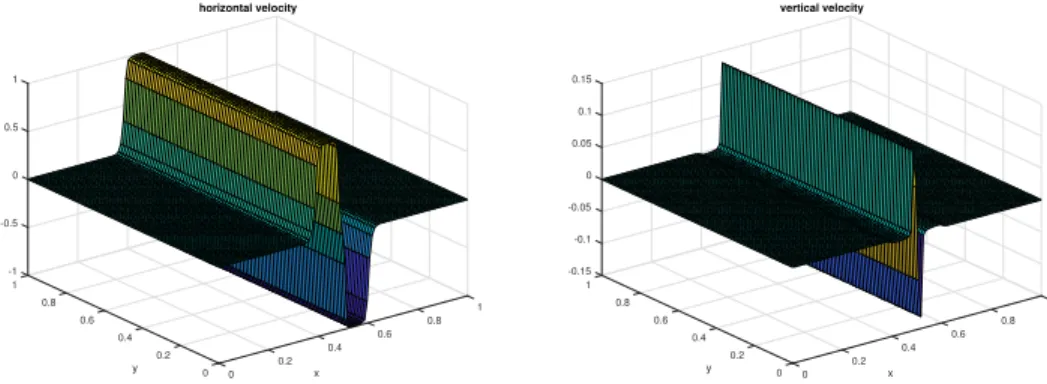
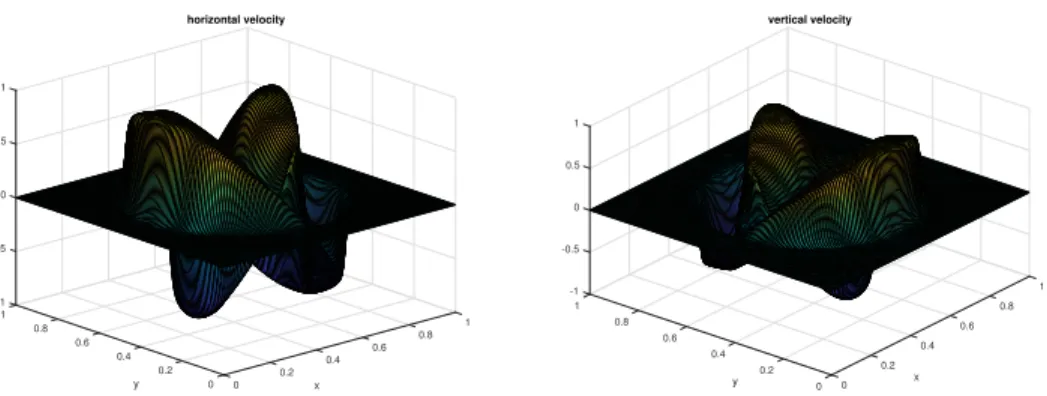
Figure

Documents relatifs
But if statement Sh fails to make sense, it seems that statement Sf does not make sense either, according to Condition1: for the terms “brain” and “left arm” occupy the
varieties up to isogeny (a free group generated by simple abelian varieties up to isogeny), is the subgroup generated by the Jacobians the whole group? It would actually suffice if
This paper presents an efficient algorithm, called FLASH, to obtain a bijective landmark aligned spherical harmonic parameterization for genus-0 closed brain sur- faces.. The three
Gibbs : les math´ ematiques du hasard au cœur de la physique ?” Conf´ erence donn´ ee dans le cadre du cycle Un texte, un math´
The matrix formed by the first, the second, and the last vector has the determinant 9, so is invertible, so its reduced row echelon form is the identity matrix, so those three
Recall that the ring Z [X] is factorial, its irreducible elements of positive degree are the non-constant poly- nomials with integer coefficients which are irreducible in Q [X ] (i.e.
Index Terms—Business to worker, multiagent system, multiagent architecture, generic service component, field trial, virtual
In this section, we also study numerically the rate of convergence of ϑ N,∆t to ϑ N and observe a weak error of order ∆t, even when the flux function is not small and not