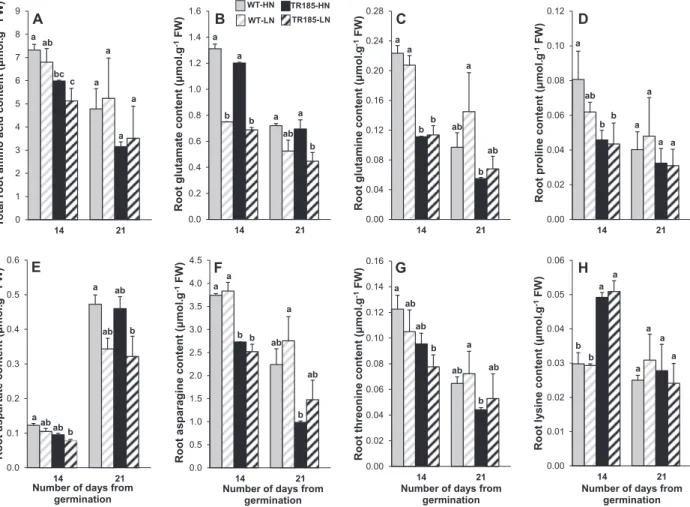
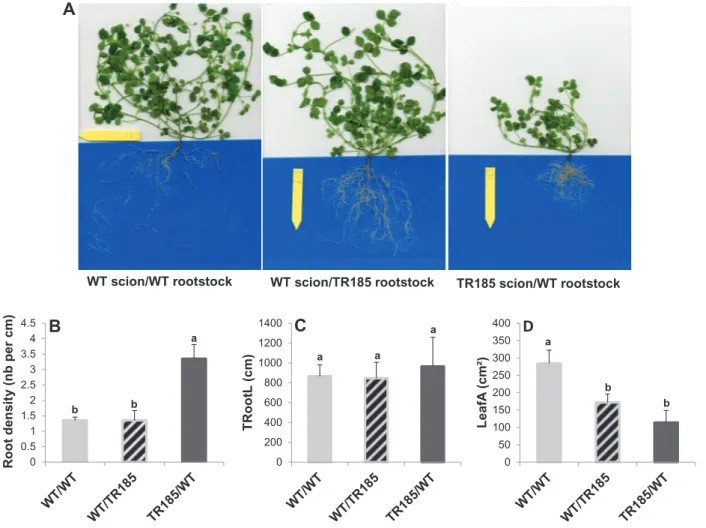
Unexpectedly low nitrogen acquisition and absence of root architecture adaptation to nitrate supply in a [i]Medicago truncatula[/i] highly branched root mutant
Texte intégral
Figure



Documents relatifs
• The internal concentration of isoflavonoids in white lupin ( Lupinus albus ) cluster roots and the exudation of isoflavonoids by these roots were investigated with respect to
in exposed root systems were similar for both species: (i) link order and number following the topology presented in [16], (ii) link diameter before each bifurcation, and diameters
Based on the topology of the root system in wheat, historical literature and experimental data, a root morphological model of wheat was established preliminarily
The three della mutants did not reveal any significant root diameter phenotype, even though in some della1 and della2 mutant roots the number of cortical cell layers was
Identification de déterminants génétiques de l’architecture racinaire et nodulaire des légumineuses et contribuant à une amélioration de la nutrition azotée.. Journées
calibration of the diffusion and advection operators; simulation results of non- centralized root growth provided by the RootTyp software (b) and by C-ROOT (c). Springer
Moreover, genes encoding ILR1, IAR3, and additional amidohydrolases, such as ILL1 and ILL2, are expressed differentially within the plant, which suggests that
To further characterize the role of MtNPF6.8 in nitrate signaling, the expression of three nitrate-inducible genes (two genes encoding nitrate reductase NR1 and NR2 and a gene