Participation of green organs to grain filling in triticum turgidum var durum grown under mediterranean conditions
Texte intégral
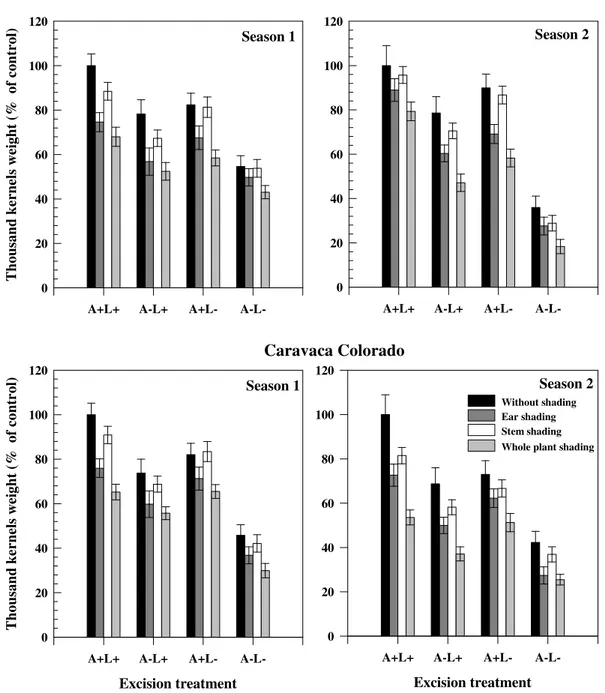
Figure



Documents relatifs
Leur ancêtre est l'égilope (Aegilops), grande céréale à un rang de grains : voici environ 500 000 ans, il s’est croisé avec Triticum uartu (engrain sauvage)
Axel is a minimalistic robot consisting of two wheels connected by a central cylindrical body, a caster arm, and an actively controlled tether passing through the caster arm
As no fully assembled batoid genome is currently available, and to better support synteny of the tandem copies in elasmobranchs, we used cDNA sequences from the thornback ray and
To possess a SCM behavior the molecular system must satisfy three key parameters: (i) its magnetic anisotropy must be uni-axial and large, (ii) efficient exchange
In keeping with the trade creation-diversion literature, we augment the model introduced by A&vW with the variables measuring MERCOSUR’s trade impact: MERCOSUR’s trade
[r]
As the durum wheat cultivars’ wet gluten content, gluten extensibility, semolina yield, the semolina’s yellow pigment content, highly depends on the growing conditions (area,
Unit´e de recherche INRIA Lorraine, Technopˆole de Nancy-Brabois, Campus scientifique, ` NANCY 615 rue du Jardin Botanique, BP 101, 54600 VILLERS LES Unit´e de recherche INRIA


