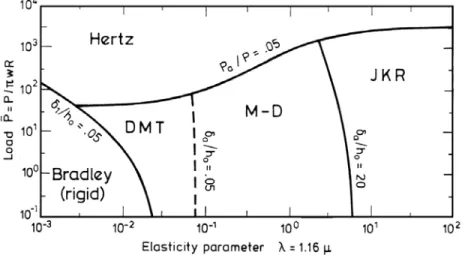
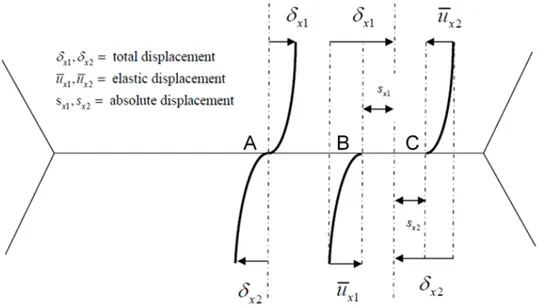
Modèles non linéaires pour l'interaction tube-support
Texte intégral
Figure
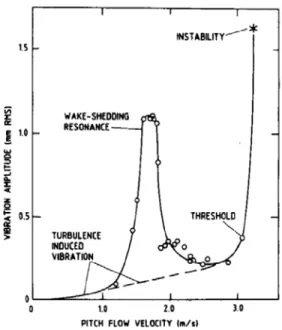
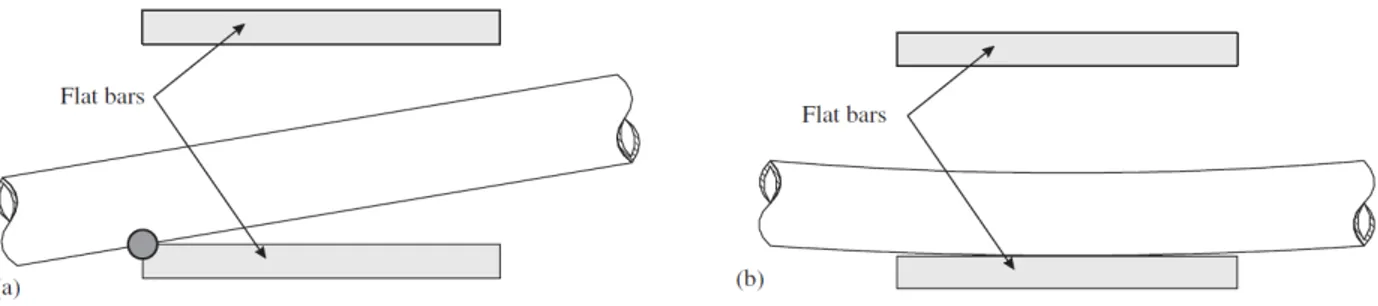
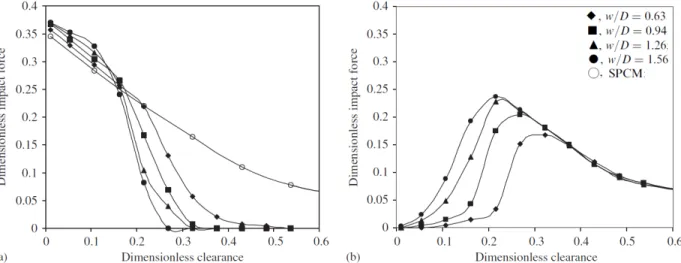

Documents relatifs
[ 22 ] The results of the last section suggest that a transient wave or a static stress increase may enhance the likelihood of an impending earthquake on a fault which presents a
Here a distinct, quasi-static mechanism is evidenced leading to quasi-periodic force oscillations during sliding contact between an elastomer block, whose surface is patterned
One of the most popular models of stick-slip oscillators consists of several masses connected by linear springs; one (or more) of the masses is in contact with a driving belt moving
Invariant slow manifolds of an Atomic Force Microscope system under the e ff ects of Lennard-Jones forces and a slow harmonic base motion. Deformation, Contact Time, and Phase
As we expect the same friction force at the tip/surface interface during a usual scan as during a lateral scan, we can link the friction signal Vr (in
Note that, if stress shadowing had not been included in our calcu- lations, the weakening functions above would not have succeeded alone in reproducing the observed slip profiles;
Based on existing data from VERT and HERMES European projects, it is possible to relate three of them to measurable parameters such as road surface macro- and microtexture,
Parametric design studies show that evolution of limit cycle amplitude can be altered by changes in the brake friction coefficient, brake force, stiffness, mass and angle.. 9