Toward a Sparse Bayesian Markov Random Field Approach to Hyperspectral Unmixing and Classification
Texte intégral
Figure


Documents relatifs
Tourneret, “Supervised nonlinear spectral unmixing using a polynomial post nonlinear model for hyperspectral imagery,” IEEE Trans- actions on Image Processing, vol. Li,
Index Terms— Hyperspectral imagery, unsupervised spectral unmixing, Hamiltonian Monte Carlo, post-nonlinear
Tourneret, “Su- pervised nonlinear spectral unmixing using a post-nonlinear mixing model for hyperspectral imagery,” IEEE Trans.. Image
Tourneret, “Supervised nonlinear spectral unmixing using a post-nonlinear mixing model for hyperspectral imagery,” IEEE Trans.. Image
Tourneret, “Supervised nonlinear spectral unmixing using a polynomial post nonlinear model for hyperspectral imagery,” IEEE Trans- actions on Image Processing, vol. Li,
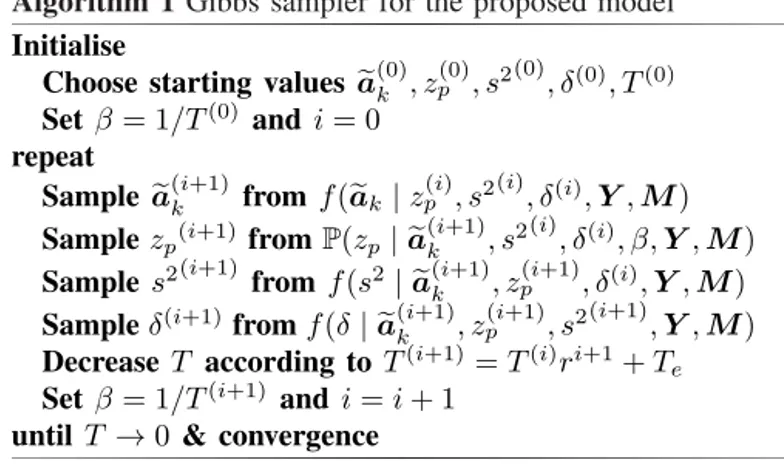
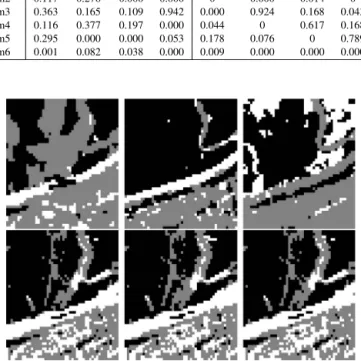
Based on a novel hierarchical Bayesian model, change detection into hyperspectral images is achieved by unmixing.. A Gibbs sampler is proposed to overcome the complexity of
Bayesian algorithm for unsupervised unmixing of hyperspectral images using a post-nonlinear model.. Yoann Altmann, Nicolas Dobigeon,
dominated by mixed pixels, even if the associated ground-truth information is only available in full-pixel form. Hence, the use of spectral unmixing presents distinctive features