A time splitting projection scheme for compressible two-phase flows. Application to the interaction of bubbles with ultrasound waves
Texte intégral
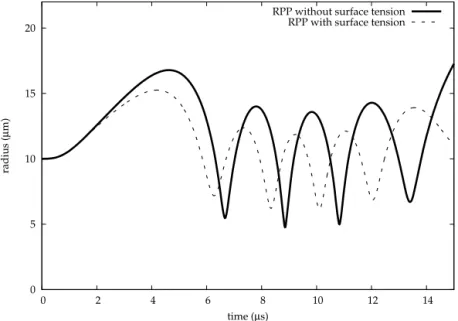
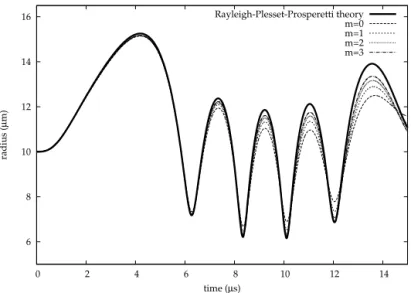
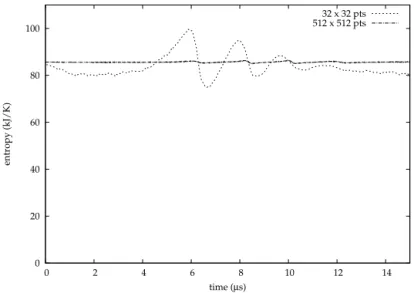
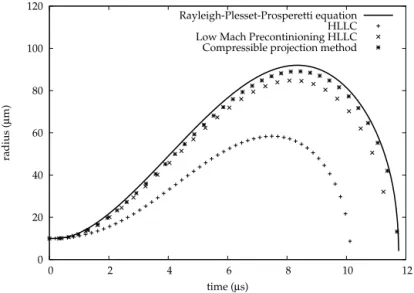
Figure



Documents relatifs
This study focuses on the development of a pressure based method able to capture compressibility effects and phase change in turbulent two-phase flow DNS, using the Coupled
27 (2005), 914–936], we propose a relaxation scheme for the numerical simulation of one-dimensional two-phase multi-component flows governed by a drift-flux model, the main features
A numerical scheme for the computation of phase transition in compressible multiphase flows..
The scheme has the following properties: it preserves constant velocity and pressure at the two-fluid interface, it preserves a perfectly sharp interface and it is fully
The compressible two-layer mixed-flows model (nicknamed CTL model in the following) is a two-fluid model which can be seen as an extension of the Baer-Nunziato model with
A Two-Dimensional Relaxation Scheme for the Hybrid Modelling of Gas-Particle Two-Phase Flows.. Kateryna Dorogan,
Using explicit schemes, one obtains a CFL condition based on the celerity of (fast) acoustic waves which typically brings large numerical diffusivity for the (slow) material waves
Regarding the CTL model (S ), the slow dynamics of the stratified regime is driven by the hydrostatic gradient found in the momentum conservation equation for the water phase while