Modelling and numerical simulation of metastable two-phase flows
Texte intégral
Figure



Documents relatifs
In dense particle laden flows we have used a similar approach, coupling a Lagrangian stochastic model for particles, to Eulerian RANS equations for the fluid.. However, albeit
A partir d’investigations dans des cas de maladies respiratoires, Friend, Thomson, Wilkie et Barnum (1977) démontrèrent que ces cas étaient dus à des infections
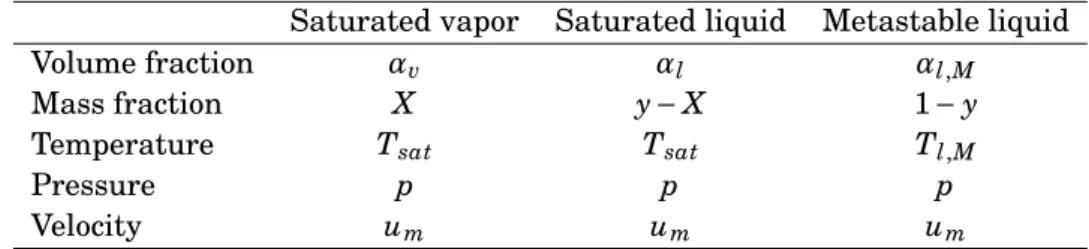
The present paper is devoted to the computation of two-phase flows using the two-fluid approach. The overall model is hyperbolic and has no conservative form. No instanta- neous
of the scheme efficiency both in 1D and 2D, we present some results of a dam break over a step, and the classical Ransom Faucet
Keywords Euler equations - Navier-Stokes equations - Two-fluid model - Finite volume methods- Roe scheme - Implicit scheme - Newton method - Preconditioner - Domain decomposition -
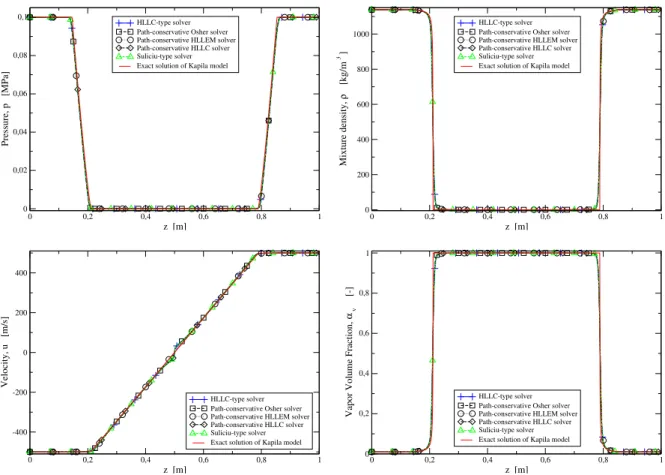
Abstract. We study the numerical solution to two-phase problems using the reduced Kapila model, i.e. In particular we focus the present study on HLLC numerical flux approximation
Data collected by the Cancer Registry of the Canton of Vaud, Switzerland, were used to estimate proportional mortality ratios (PMR) and mortality odds ratios (MOR) for various
To achieve this purpose, the whole genome of the argane tree has been sequenced using Illumina HiSeq Xten, and PacBio RS II technologies, the genome size estimated using