Modelling Environmental Effect Dependencies with Principal Component Analysis and Bayesian Dynamic Linear Models
Texte intégral
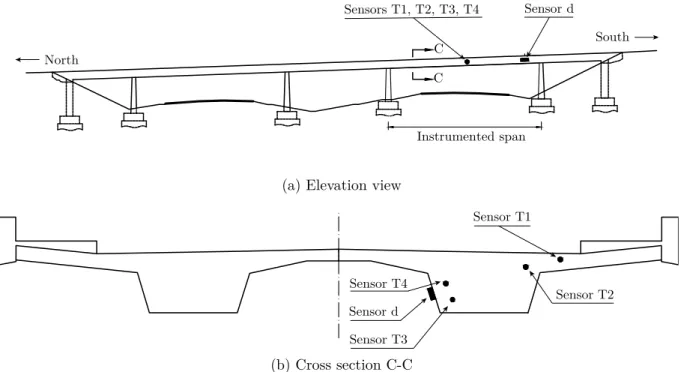
Figure


Documents relatifs
The local feature extractors together with the coordinating linear maps provide a global non-linear map from the data space to the latent space and back.. Learning the mixture is
The problems as well as the objective of this realized work are divided in three parts: Extractions of the parameters of wavelets from the ultrasonic echo of the detected defect -
The problems as well as the objective of this realized work are divided in three parts: Extractions of the parameters of wavelets from the ultrasonic echo of the detected defect -
Beyond simple bounds derived from base policies, the only theoretical results given explicitly for rollout algorithms are average-case results for the breakthrough problem
L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, émanant des
L’archive ouverte pluridisciplinaire HAL, est destinée au dépôt et à la diffusion de documents scientifiques de niveau recherche, publiés ou non, émanant des
Our new methodology represents a promising alternative over the extensively used sticky air approximation since it overcomes several of its major draw- backs, namely (i) the method