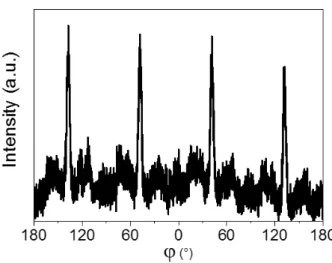
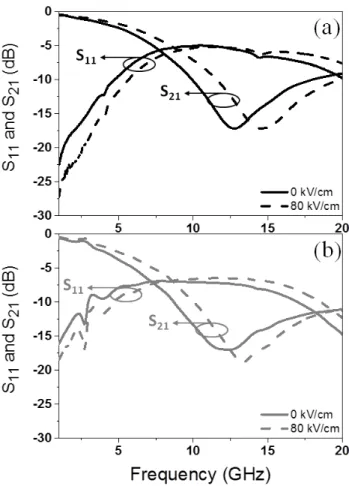
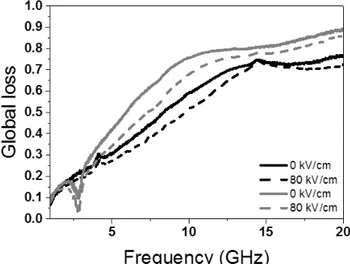
KxNa1−xNbO3 perovskite thin films grown by pulsed laser deposition on R-plane sapphire for tunable microwave devices
Texte intégral
Figure
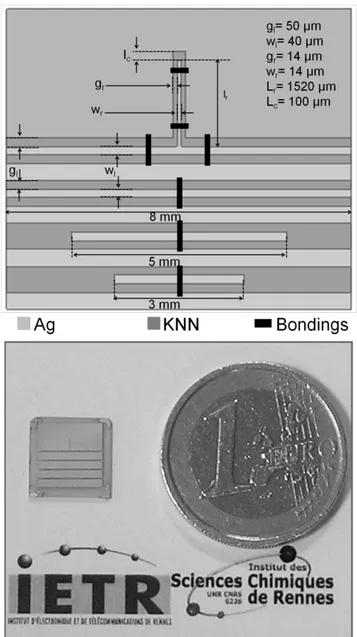
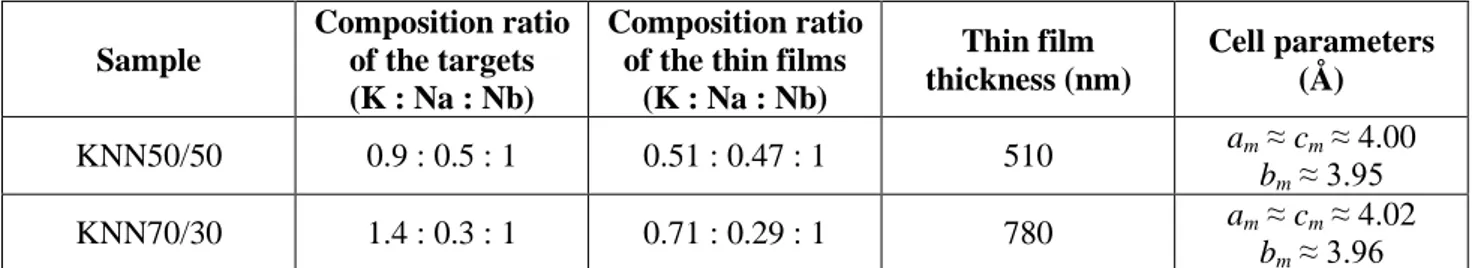
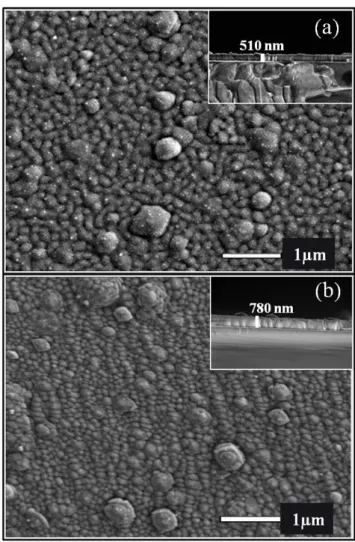
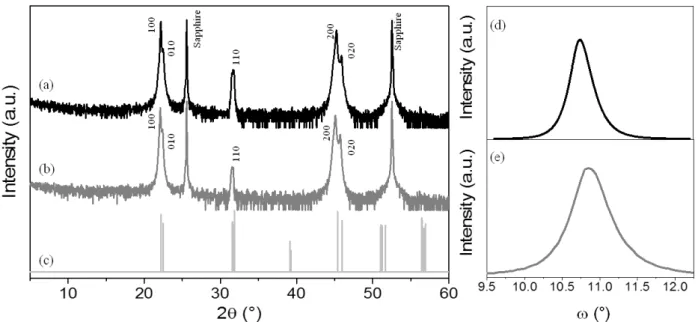
Documents relatifs
Epitaxial growth and properties of lead-free ferroelectric Na0.5Bi0.5TiO3 thin films grown by pulsed laser deposition on various single crystal substrates.. 2012
Static and Dynamic Magnetic Properties of Single-Crystalline Yttrium Iron Garnet Films Epitaxially Grown on Three Garnet Substrates. Stress-induced perpendicular magnetization
The key finding of this first prospective, observational 10-year follow-up study including community-dwelling patients visiting their GP for a respiratory infection is that
(It must be emphasized that such differences in the formant patterns do not affect the vowel identity itself.) Conversely, there are examples of vocalizations within one speaker
Polycrystalline zinc oxide (ZnO) thin films have been deposited at 450˚C onto glass and silicon substrates by pulsed laser deposition technique (PLD).. The effects of glass
Abstract : Undoped and Co-doped ZnO (CZO) polycrystalline thin films (Co: 3, 5 at.%) have been deposited at 450ºC onto glass substrates using pulsed laser deposition method..
X-ray diffraction patterns showed that the Co- doped ZnO films crystallize in a hexagonal wurtzite type structure with a strong (002) orientation, and the grain sizes calculated
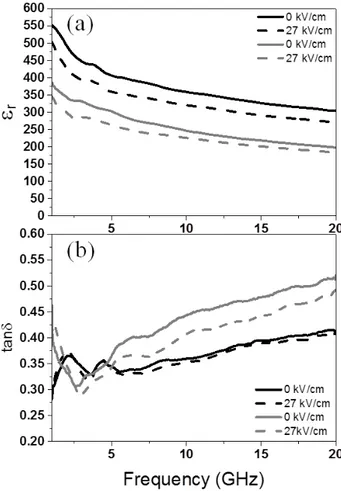
Finally, at microwave frequencies, domain wall motion (vibration and pinning/unpinning) still contributes to the material’s dielectric properties. Despite being highly tunable,