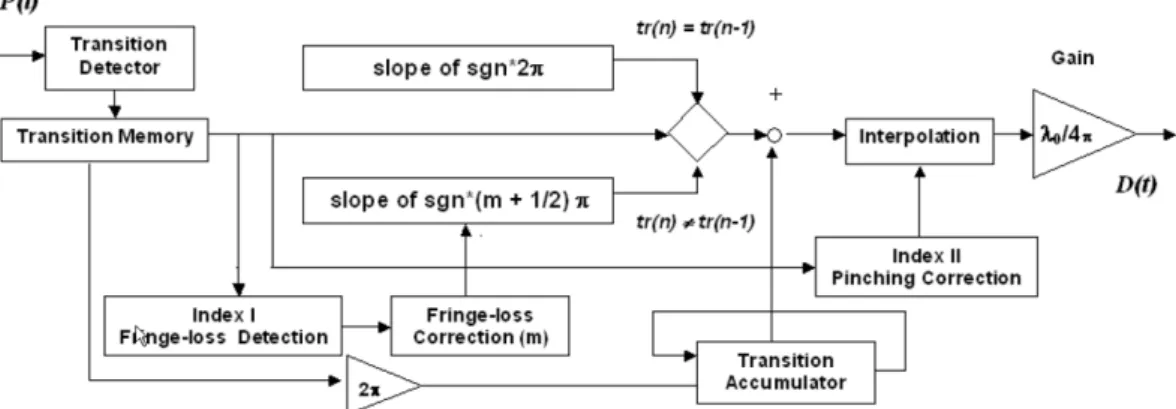
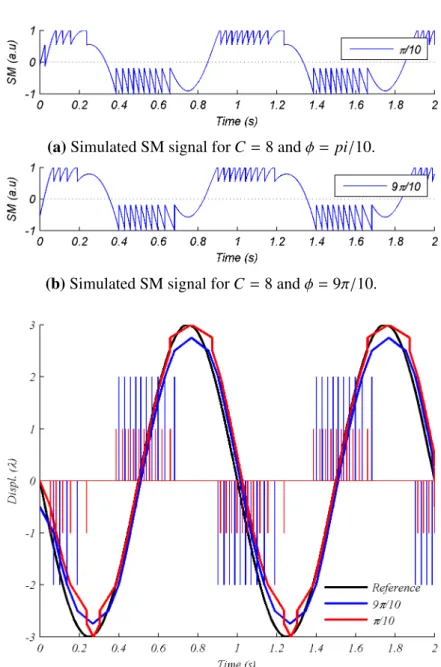
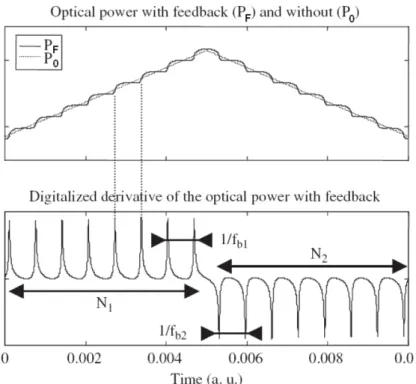
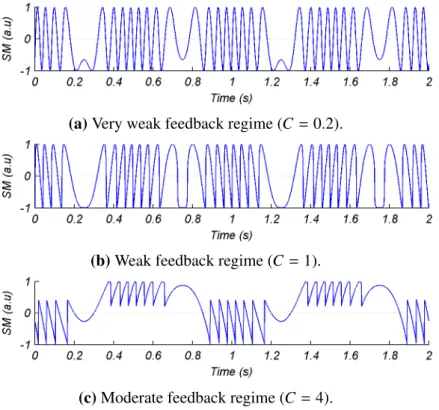
Analysis and implementation of algorithms for embedded self-mixing displacement sensors design
Texte intégral
Figure

Documents relatifs
3D mechanical analysis of aeronautical plain bearings: Validation of a finite element model from measurement of displacement fields by digital volume correlation and
Such a method has been used even in 2008 by Ottonelli for a 3 Degrees-of-Freedom motion sensor based on SM effect [ 33] for the simultaneous measurement of the linear displacement
This SM sensor subject to weak feedback has been tested in comparison with a commercial vibrometer in order to measure the frequency response function (FRF) of a plate with a
curve) that the corrupted signal i.e. However, a correct target displacement measurement has been made by our real-time SSA-SM sensing system as indicated by the blue curve
Hence in order to have a digital representation of the displacement to be measured, the current implementations involve two main components, namely the capacitive-to-
An improved sensor unit assembly provides a secure, pressurized contact with the patient's skin while protecting the optical components and wires from the external
Further, since currently the autofocus algorithm itself is only performed once, it was verified that maximum target displacement span after having locked to moderate feedback regime
Abstract A combination of optical feedback self-locking of a continuous-wave distributed feedback diode laser to a V-shaped high finesse cavity, laser phase modulation at a